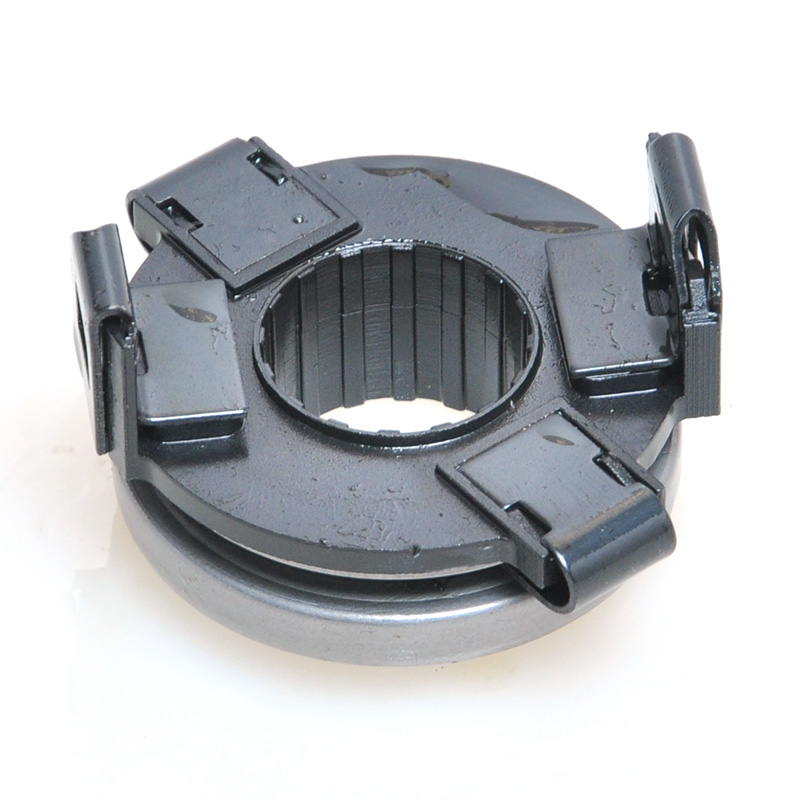
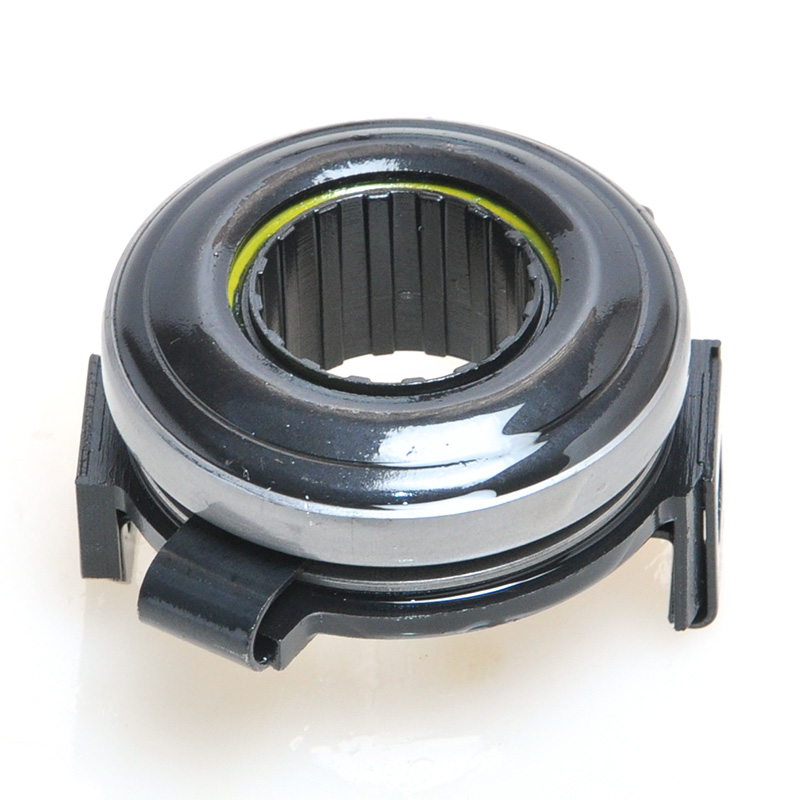
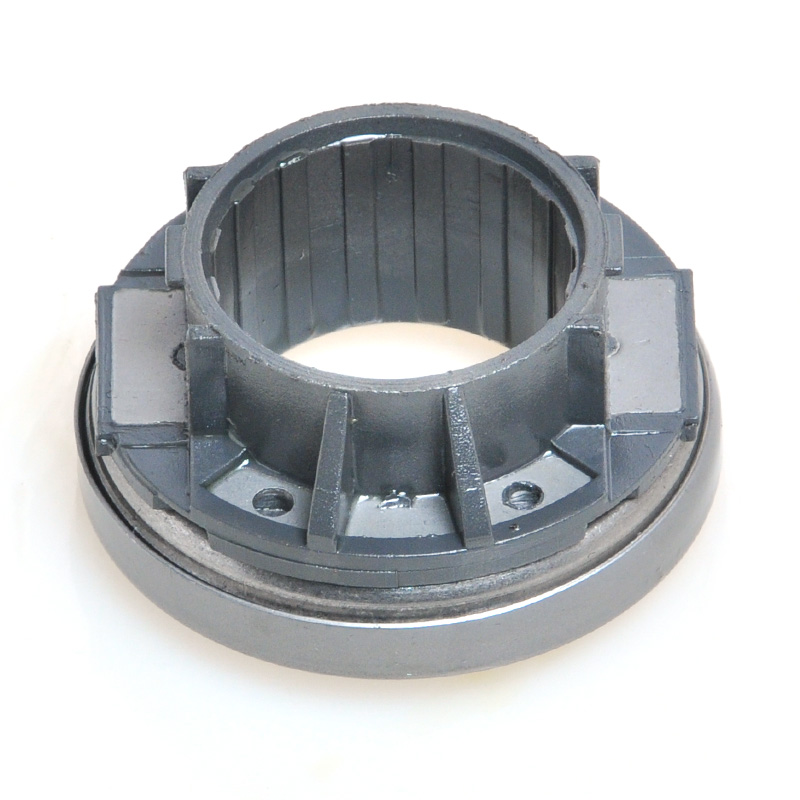
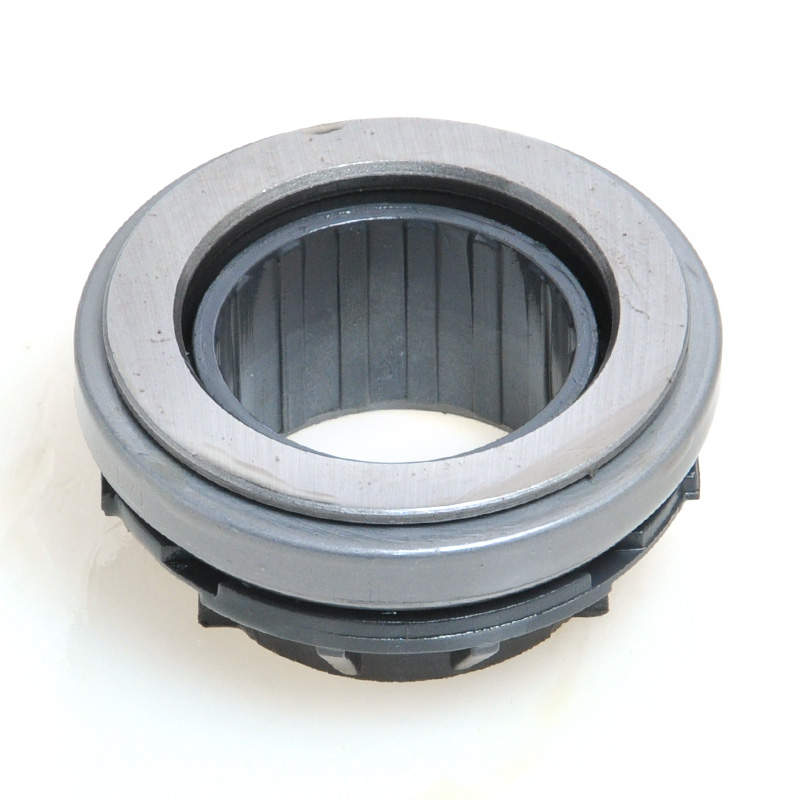
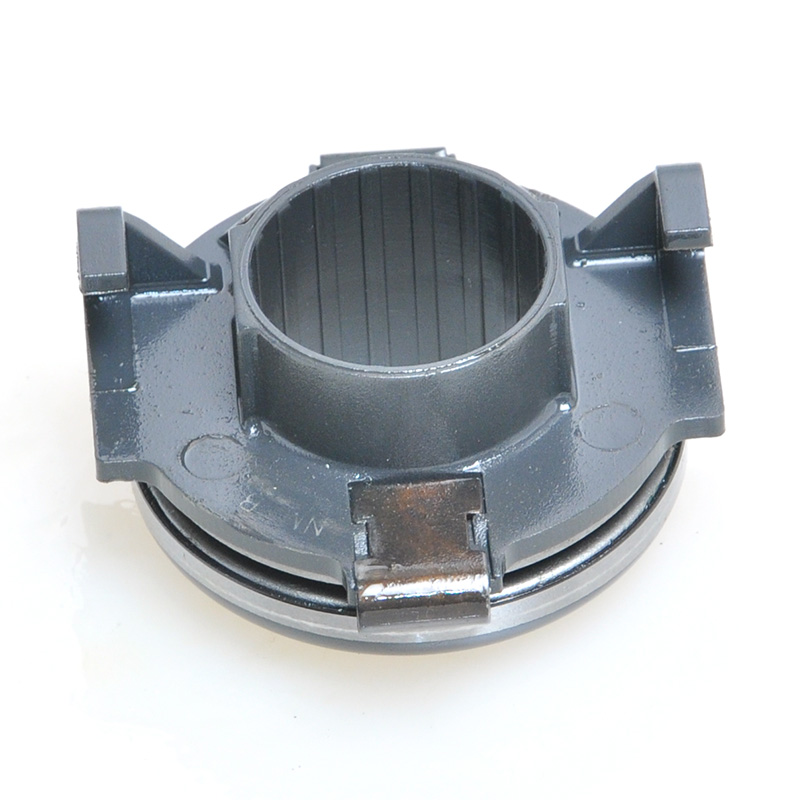
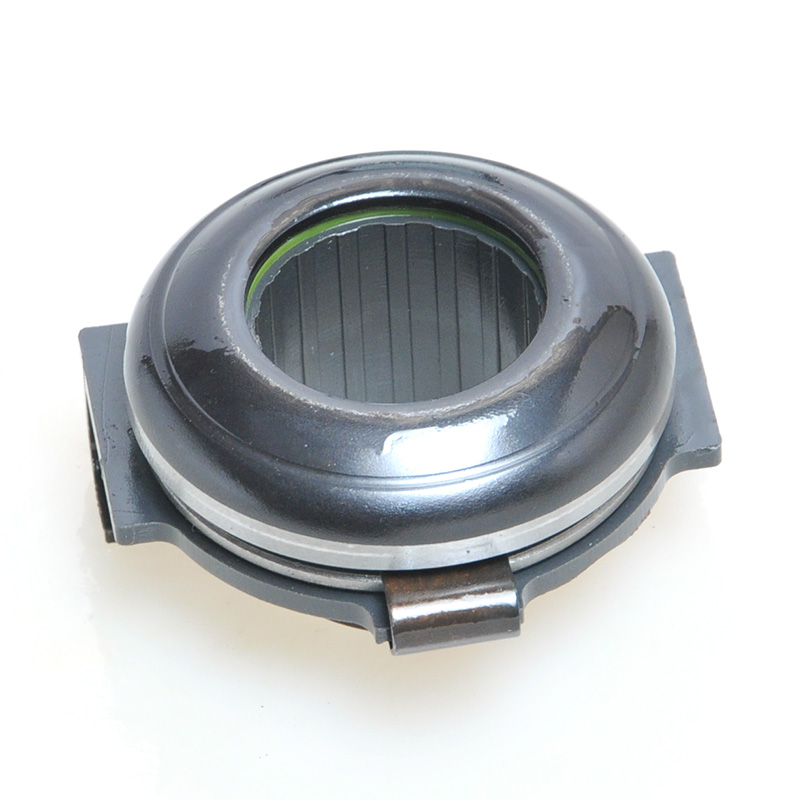
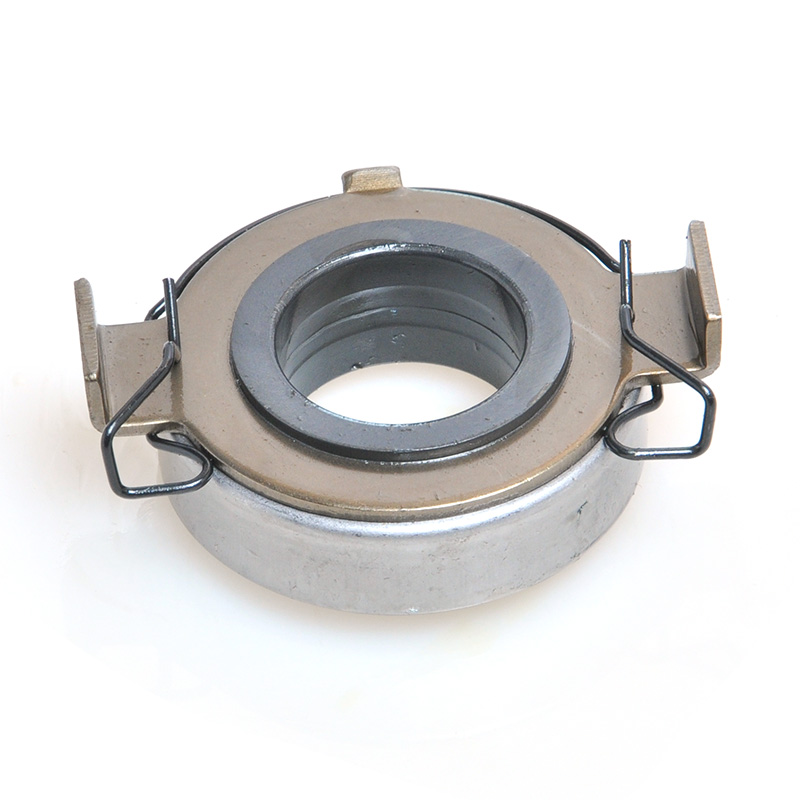
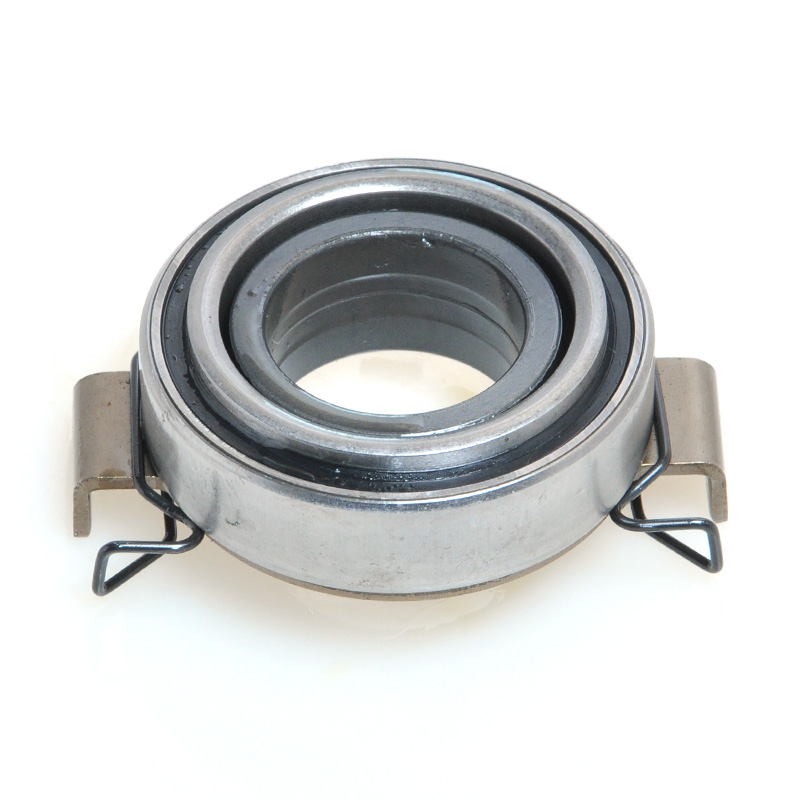
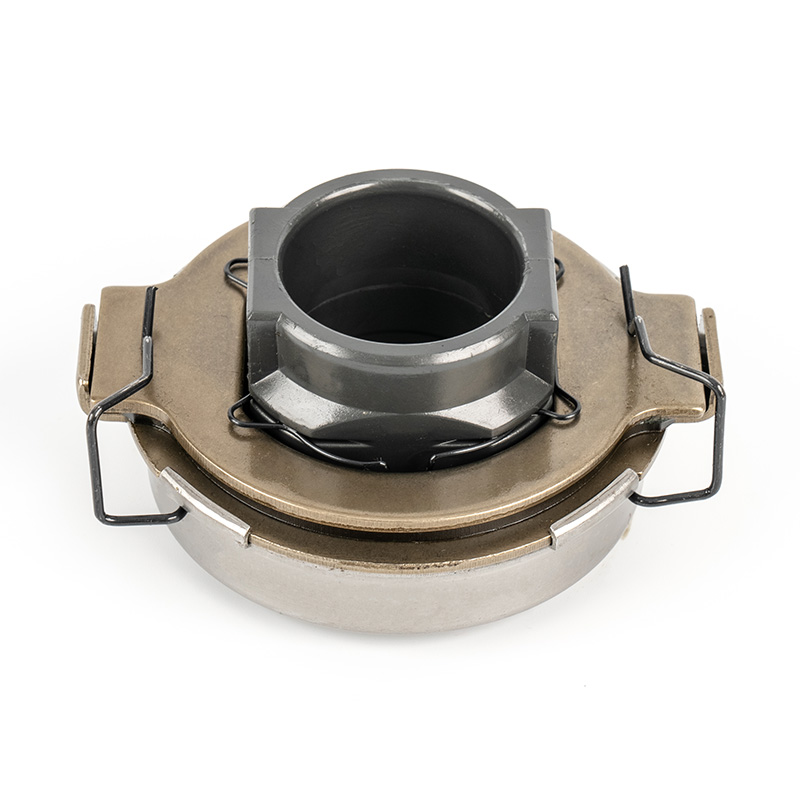
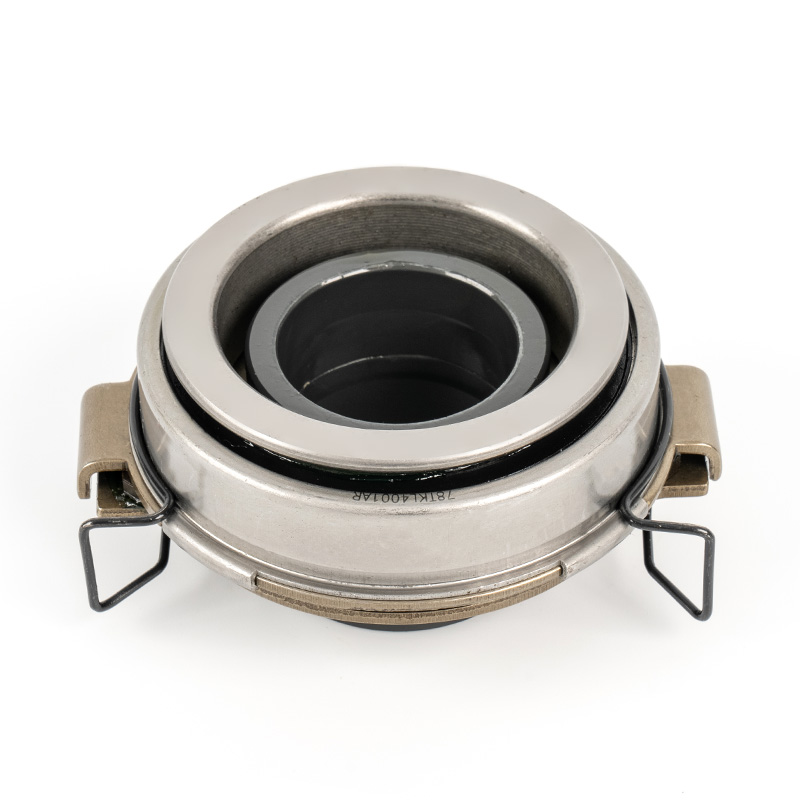
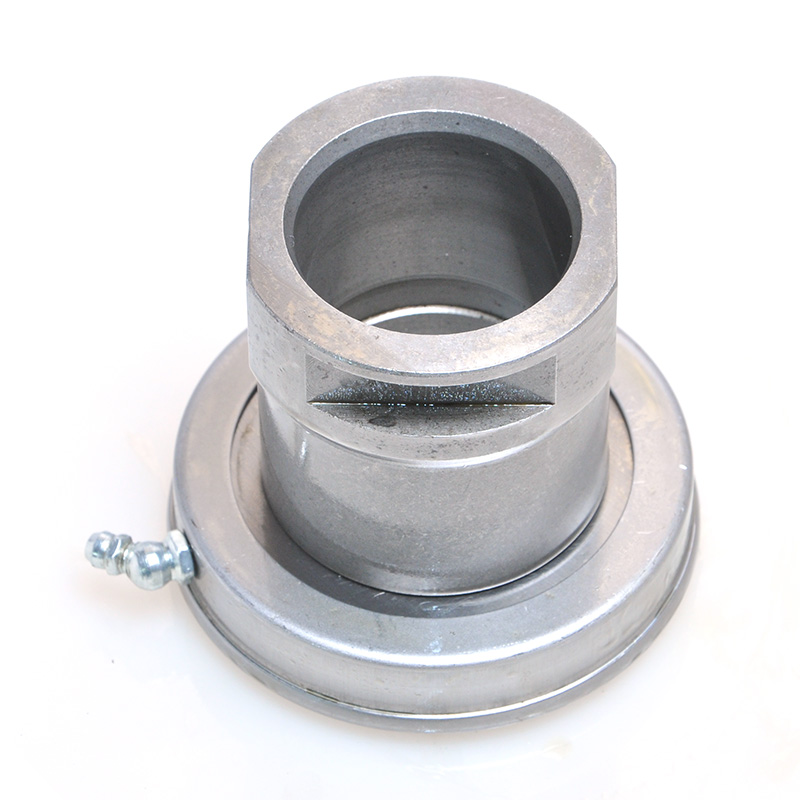
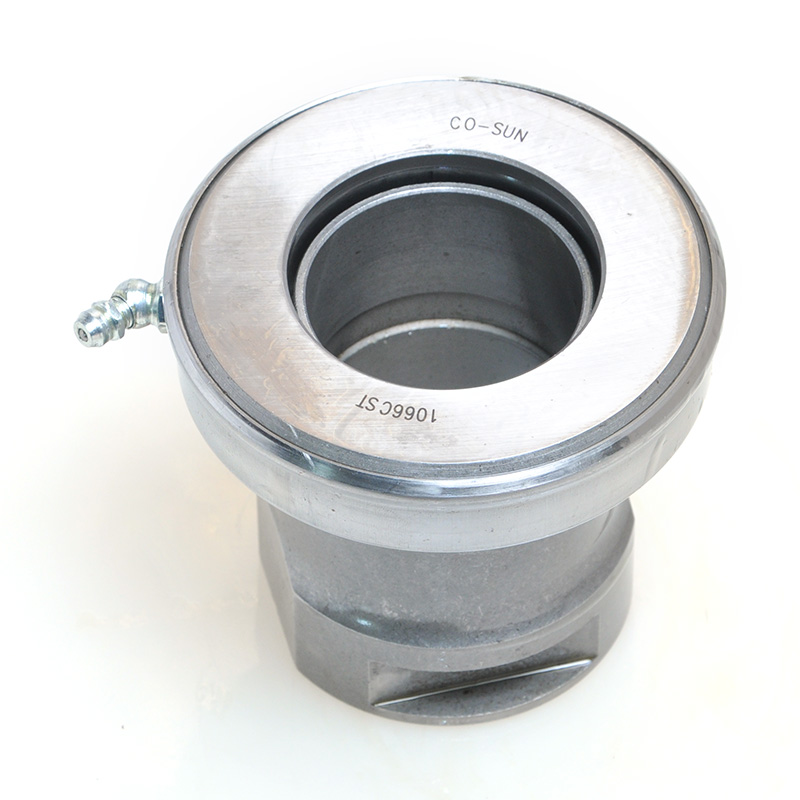
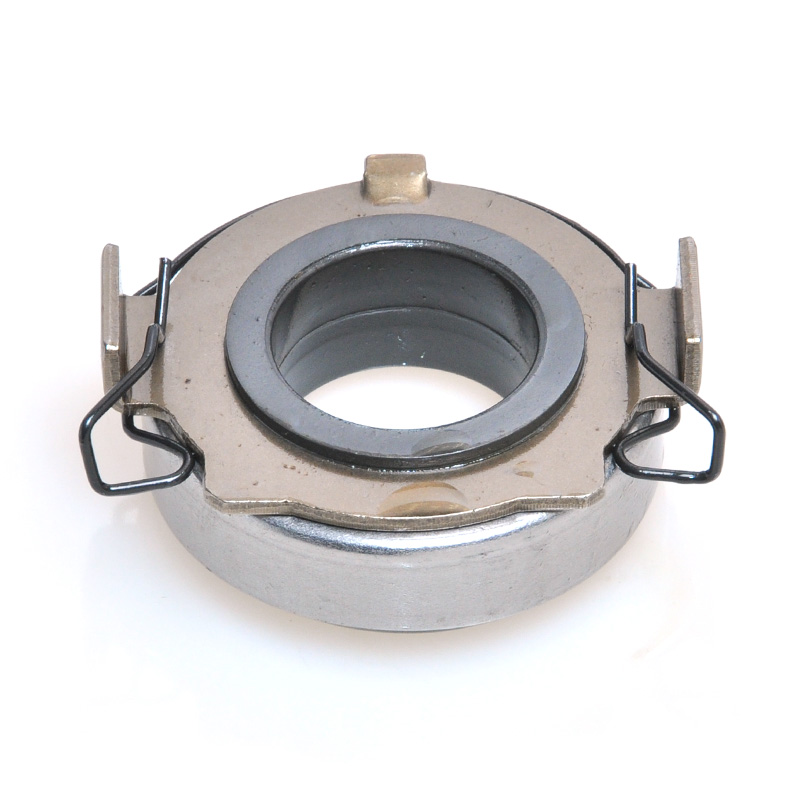
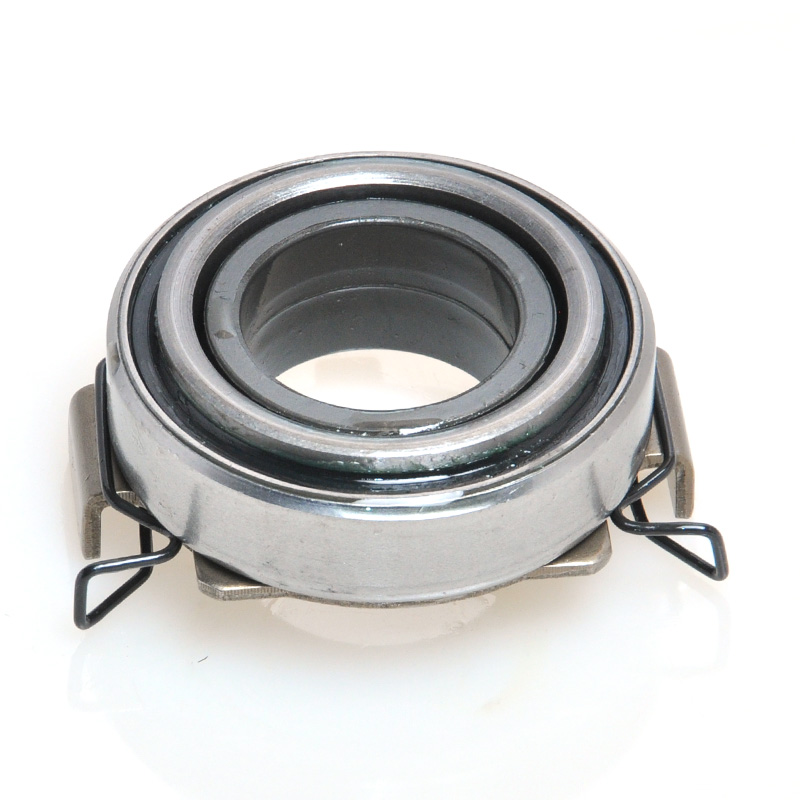
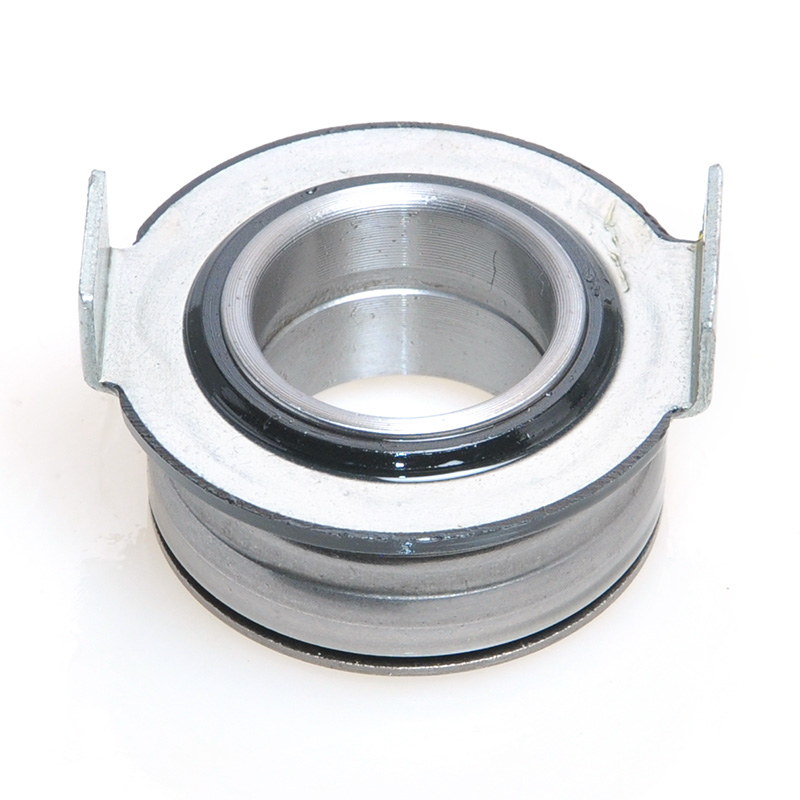
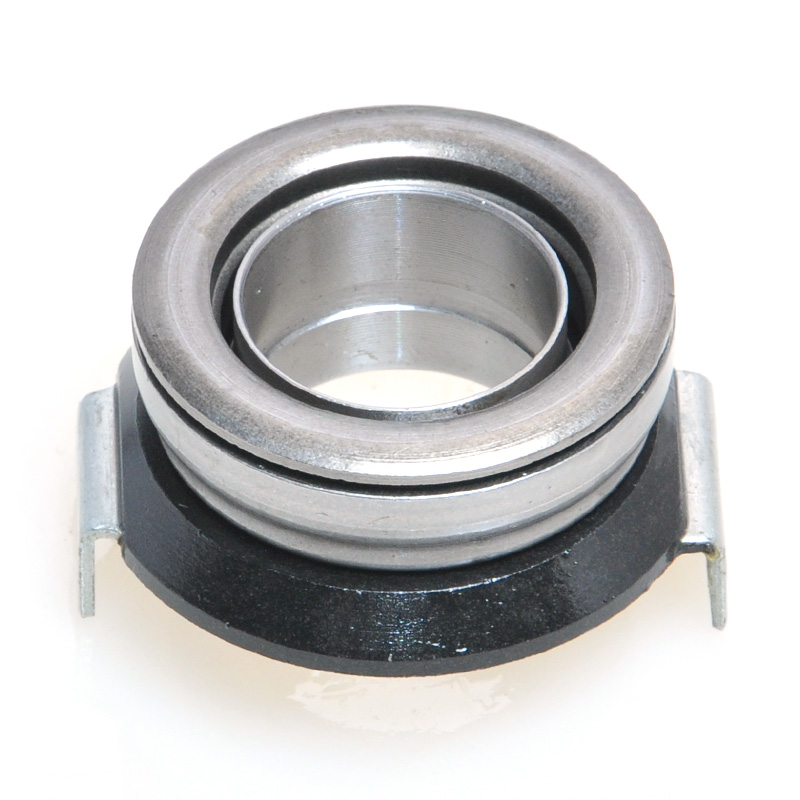
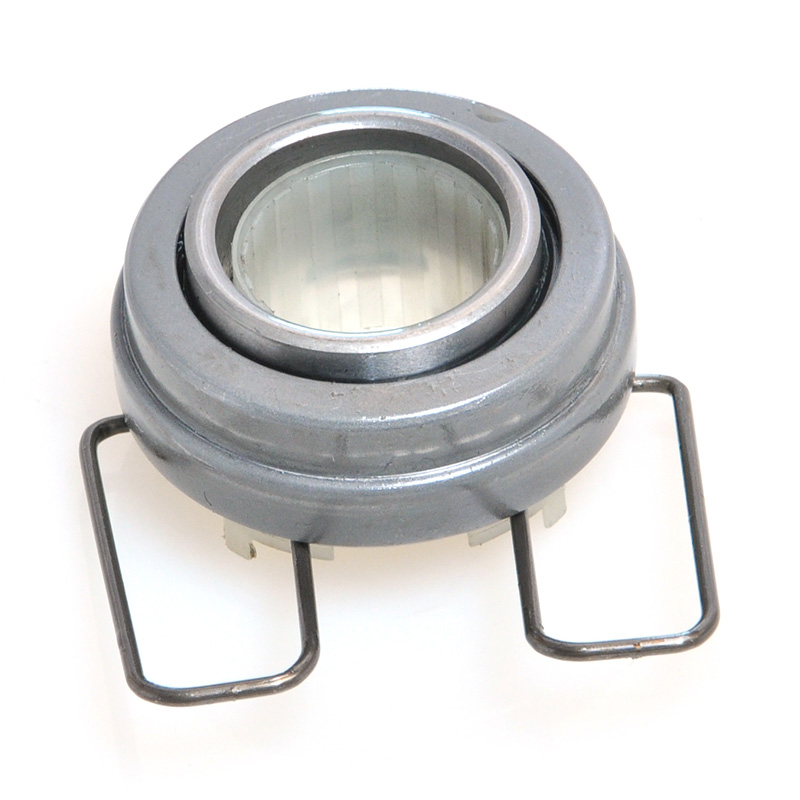
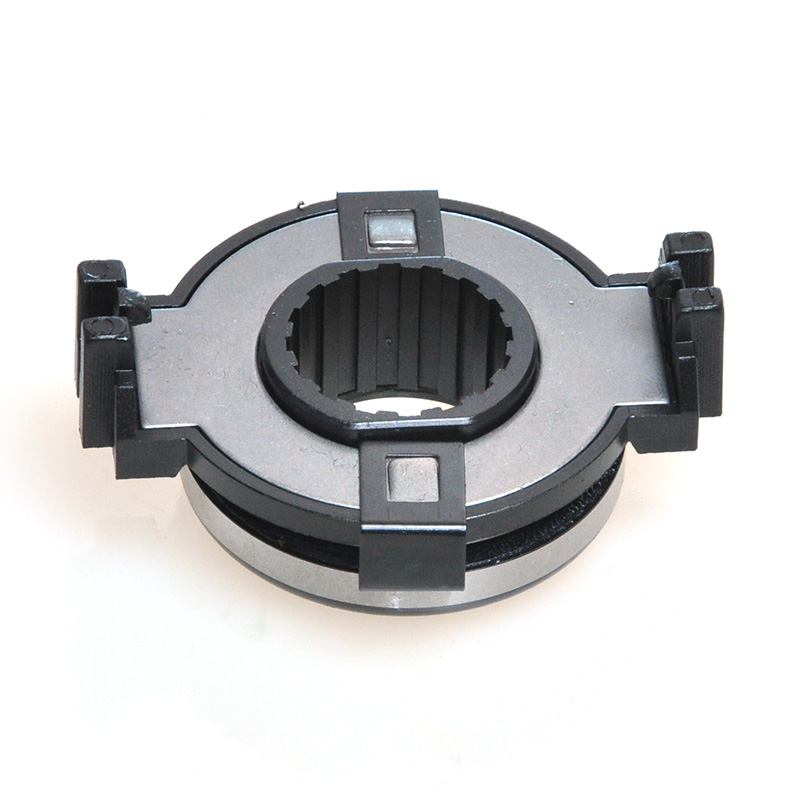
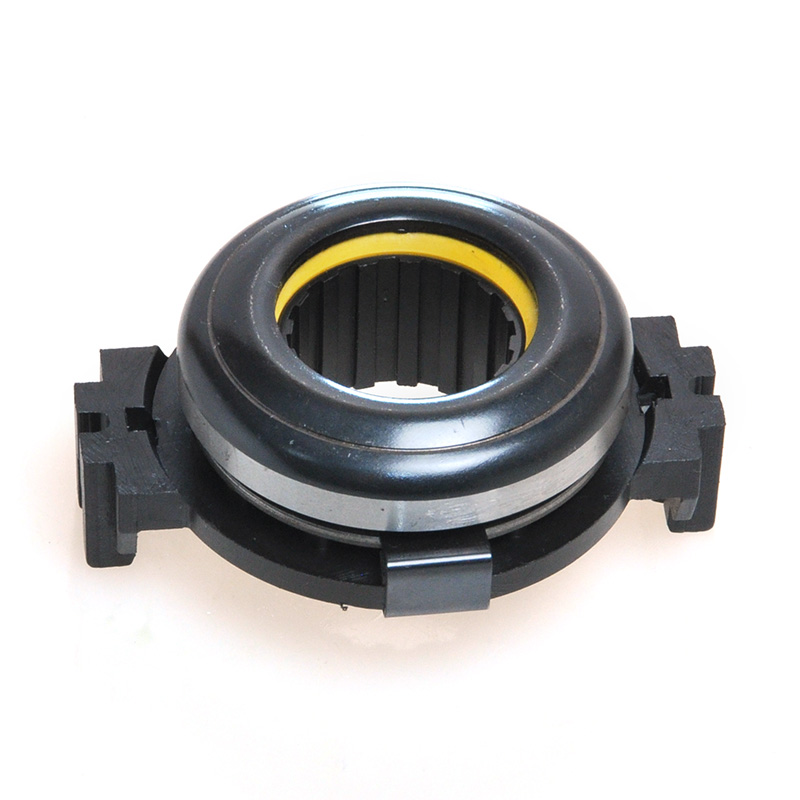
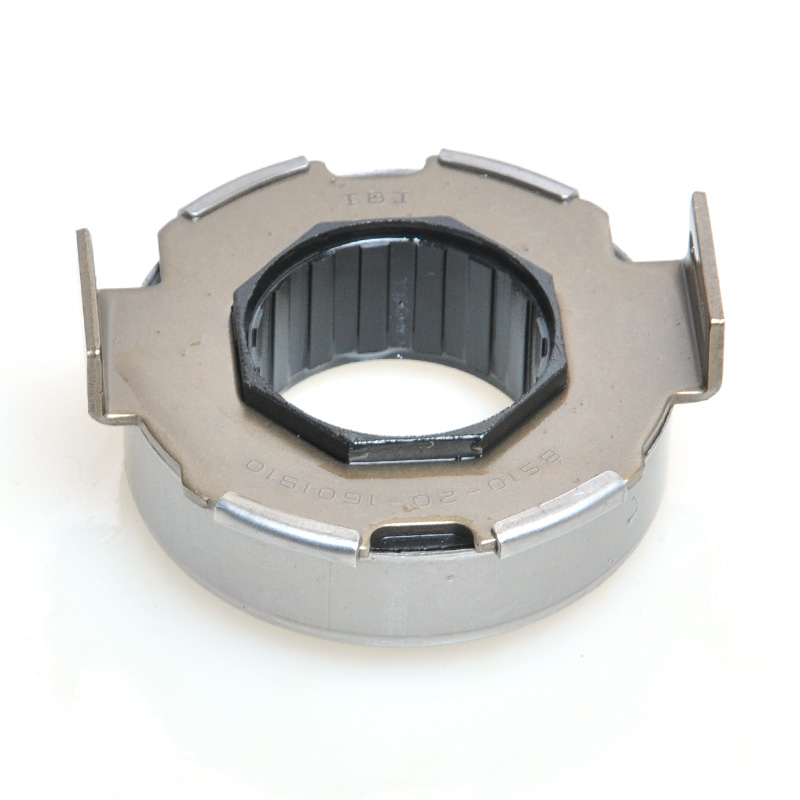
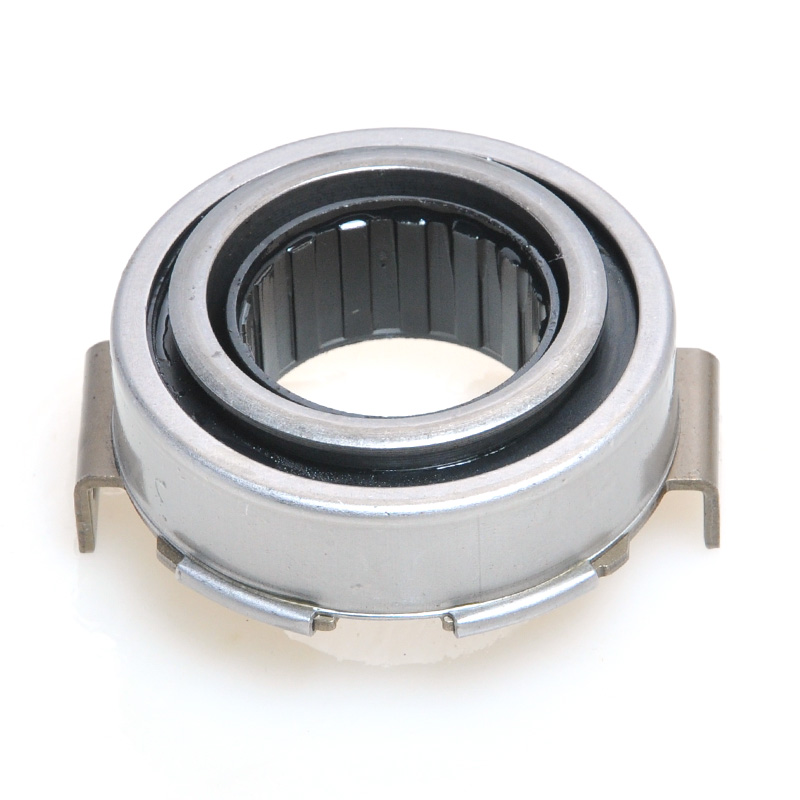
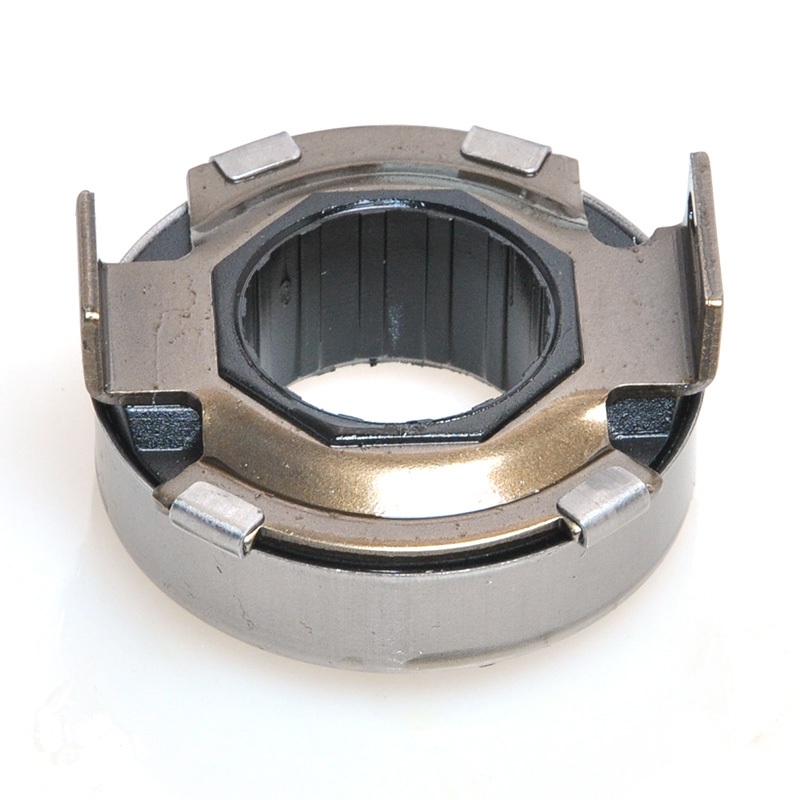
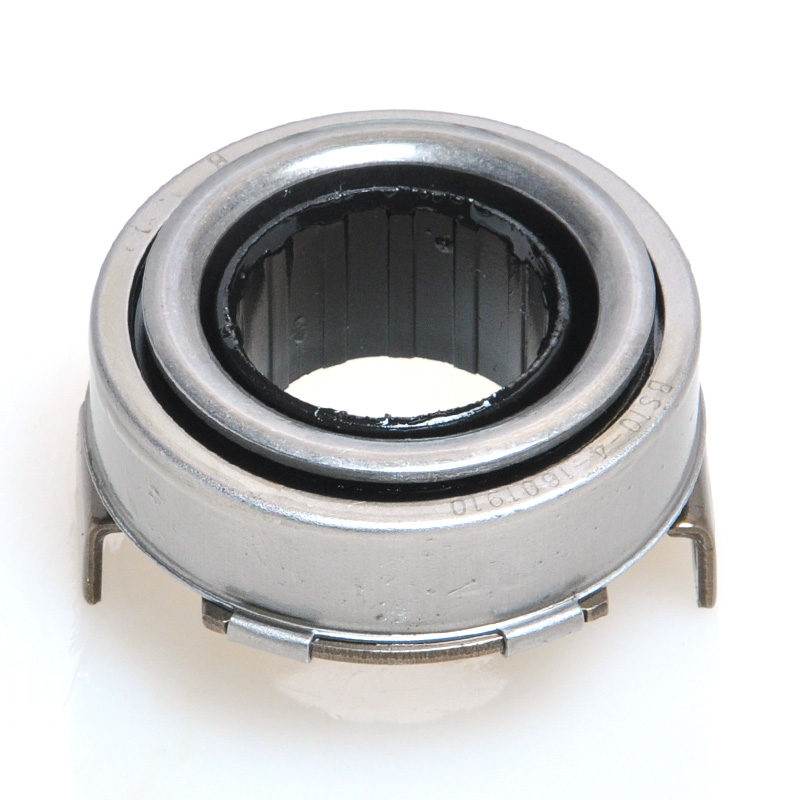
When people discover a problem with their clutch release bearing, their first reaction is often, "Can I still manage to drive it for a while?" While the car might not be completely incapacitated yet, driving with a faulty clutch release bearing is like carrying a ticking time bomb. Here's an analysis of driving with ...
READ MORE-
-
Although clutch release bearings are designed to be durable, they are also quite delicate, and many everyday habits can unknowingly shorten their lifespan. Here are some of the main reasons for their damage: 1. The Habit of Keeping Your Foot on the Clutch Pedal This is the most common cause of bearing damage. Many dr...
READ MORE -
The cost of replacing a clutch release bearing (also commonly called a release bearing or thrust bearing) mainly consists of two parts, but the most painful part is often not the cost of the part itself, but the expensive labor costs. Here's a breakdown of the repair costs: 1. Cost of the part itself Bearing unit pri...
READ MORE
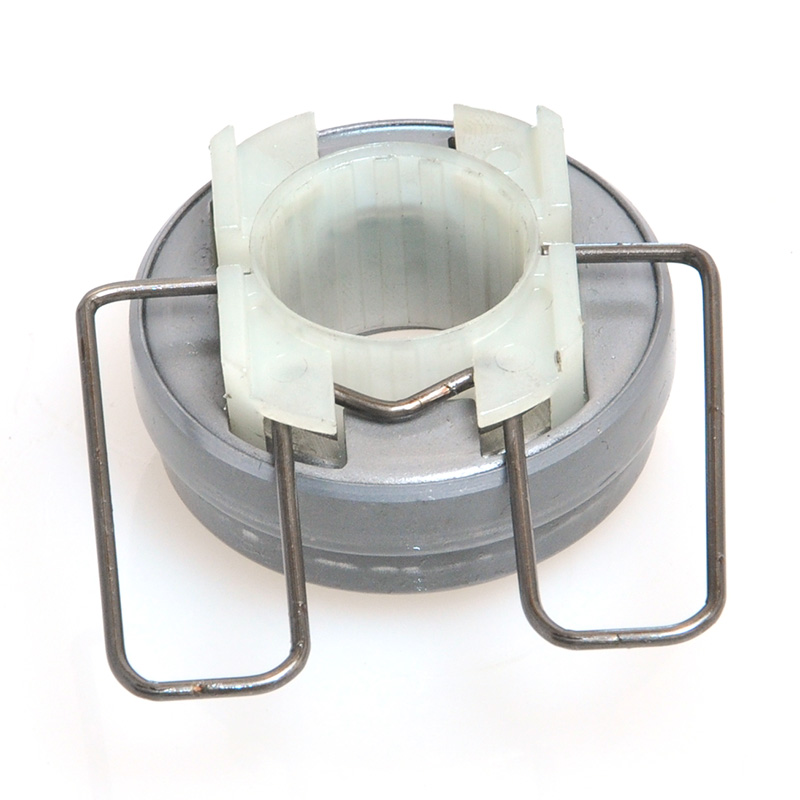
A mechanical clutch release bearing, also known as a throwout bearing, is a critical component in manual transmission systems. It facilitates the disengagement of the clutch by transmitting force from the clutch linkage to the pressure plate, enabling smooth gear shifts.
Concept and Function
The mechanical clutch release bearing is a specialized bearing assembly typically positioned between the clutch fork and the diaphragm spring or pressure plate fingers in a clutch system. Its primary function is to apply force to the clutch mechanism when the clutch pedal is depressed, thereby disengaging the clutch disc from the flywheel. This action interrupts power transmission from the engine to the transmission, allowing for gear changes. The bearing must withstand high axial loads and rotational speeds while maintaining minimal friction. Components often include a bearing race, rollers or balls, and a housing designed to interface with the clutch fork. Failure to operate correctly can lead to clutch slippage, noise, or complete transmission failure.
Types of Mechanical Clutch Release Bearings
Mechanical clutch release bearings are categorized based on design and actuation methods. Common types include:
Push-Type Release Bearings: These bearings apply force in the direction of the engine when the clutch pedal is engaged. They are commonly used in systems where the clutch fork pushes the bearing against the pressure plate levers.
Pull-Type Release Bearings: In these systems, the bearing pulls the pressure plate away from the clutch disc when activated. This design is often found in high-torque applications, such as heavy-duty vehicles, due to its ability to handle greater loads.
Integrated Release Bearings: Some modern designs incorporate the bearing into a single unit with the clutch slave cylinder or other components, though this is more common in hydraulic systems. Mechanical versions may feature sealed or pre-lubricated designs to reduce maintenance.
Variations also exist in materials, with bearings typically constructed from hardened steel or composite materials to enhance durability and heat resistance.
Applications
Mechanical clutch release bearings are predominantly used in vehicles and machinery with manual transmissions. Applications include:
Automotive Systems: Passenger cars, trucks, and buses rely on these bearings for clutch operation. Their simplicity and cost-effectiveness make them suitable for mass-produced vehicles.
Industrial Machinery: Equipment such as agricultural tractors, construction vehicles, and industrial presses often incorporate mechanical release bearings due to their robustness and ease of repair.
Motorcycles and Light Vehicles: Smaller-scale applications use compact bearing designs to accommodate space constraints.
The selection of a bearing type depends on factors like load capacity, environmental conditions, and design specifications of the clutch system.
Comparison with Other Clutch Release Systems
Mechanical clutch release systems are often compared to hydraulic systems. Key distinctions include:
Actuation Mechanism: Mechanical systems use cables, rods, or levers to transfer force from the clutch pedal to the bearing, whereas hydraulic systems utilize fluid pressure through a master and slave cylinder. Mechanical systems are generally simpler in design but may require more physical effort from the driver.
Efficiency and Response: Hydraulic systems provide smoother and more consistent engagement, especially in high-load scenarios, due to reduced friction and self-adjusting properties. Mechanical systems, however, offer direct feedback and are less prone to fluid-related failures like leaks.
Maintenance and Durability: Mechanical bearings may experience wear in linkage components, necessitating periodic adjustment. Hydraulic systems require fluid maintenance but often have longer service intervals under ideal conditions.
Both systems have distinct advantages; mechanical versions are valued for their simplicity and lower cost, while hydraulic systems excel in performance and comfort.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages of mechanical clutch release bearings include:
Simplicity in design, leading to easier diagnosis and repair.
Lower manufacturing and maintenance costs compared to hydraulic alternatives.
Immediate driver feedback, which can enhance control in specific driving conditions.
Disadvantages involve:
Increased pedal effort in high-load applications, potentially causing driver fatigue.
Susceptibility to wear in mechanical linkages, requiring regular inspection and adjustment.
Limited performance in applications demanding precise modulation, such as racing or heavy towing.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Proper maintenance extends the lifespan of mechanical clutch release bearings. Recommendations include:
Regular inspection for wear, noise, or play in the clutch linkage.
Lubrication of pivot points and bearings as specified by manufacturer guidelines.
Adjustment of clutch free play to prevent premature bearing failure.
Common issues and solutions:
Squealing or Grinding Noises: Often indicates bearing wear or inadequate lubrication. Replacement is typically required.
Difficulty Shifting Gears: May result from a misadjusted linkage or worn bearing. Inspection of the entire clutch system is advised.
Clutch Slippage: Can be caused by a failing bearing not fully disengaging the clutch. Diagnosis should include checking for hydraulic issues in mixed systems.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the primary role of a mechanical clutch release bearing?
It disengages the clutch by applying force to the pressure plate, allowing gear changes without grinding.
How long do these bearings typically last?
Lifespan varies based on usage, but they generally last between 50,000 to 100,000 miles under normal driving conditions.
Can a worn release bearing damage other clutch components?
Yes, failure to replace a worn bearing can lead to damage to the pressure plate, clutch disc, or flywheel due to improper engagement.
Is it possible to lubricate a mechanical release bearing?
Some designs are pre-lubricated and sealed, while others may allow lubrication during service. Always refer to the vehicle's manual for specifications.
What are the signs of a failing release bearing?
Symptoms include unusual noises (e.g., rattling or squealing) when the clutch pedal is depressed, difficulty shifting, or a vibrating pedal.
As a core manufacturer of this essential component, Xinchang Heyang Auto Parts Co., Ltd. produces clutch release bearings renowned for their precision and durability. Our product line includes over 300 types of non-standard bearings, designed for compatibility with vehicles from Japan, Korea, Germany, the USA, and other major regions. Leveraging advanced production equipment and a stringent management system, we achieve an annual production capacity of 1.2 million pieces, with each bearing backed by a quality assurance of 50,000 kilometers or more.
Trusted by clients across the Middle East, Iran, Southeast Asia, South America, and Europe, we operate on the principles of "Customer demand first" and meticulous attention to every detail. We sincerely welcome your inquiries and look forward to building a productive partnership.
 +86-13867573512
+86-13867573512