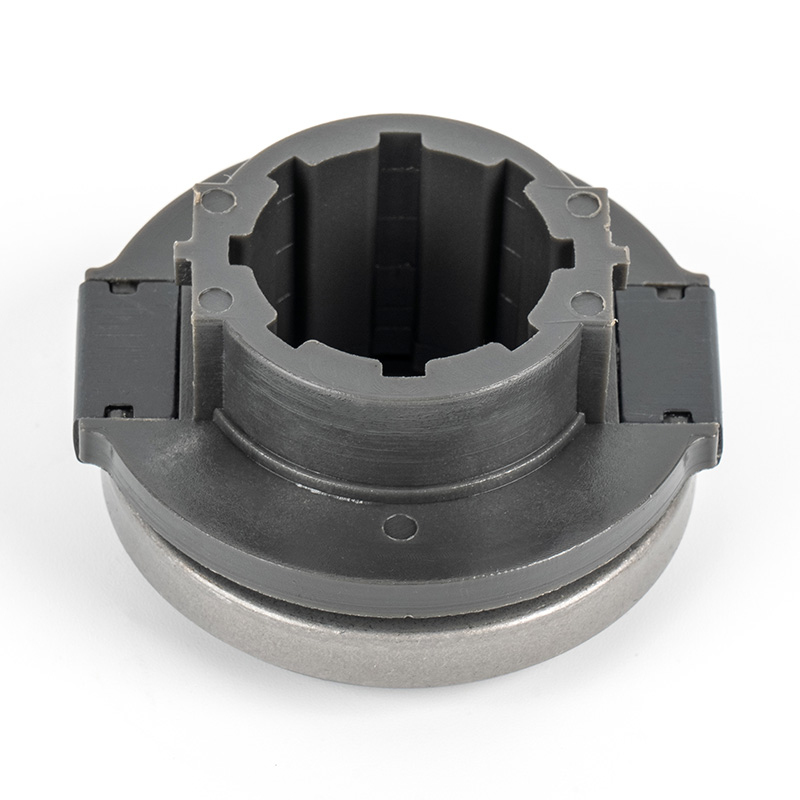
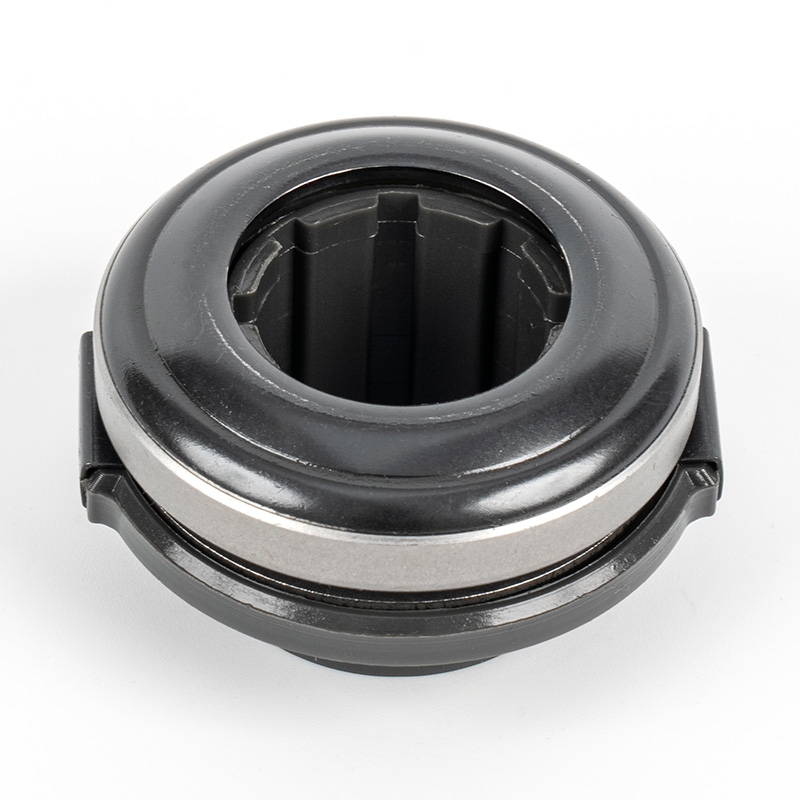
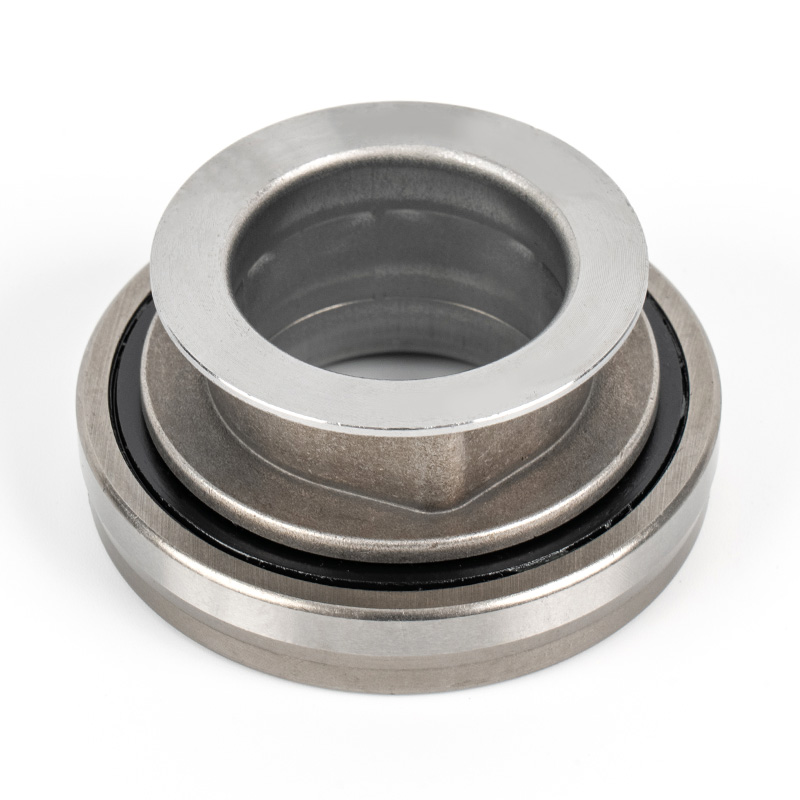
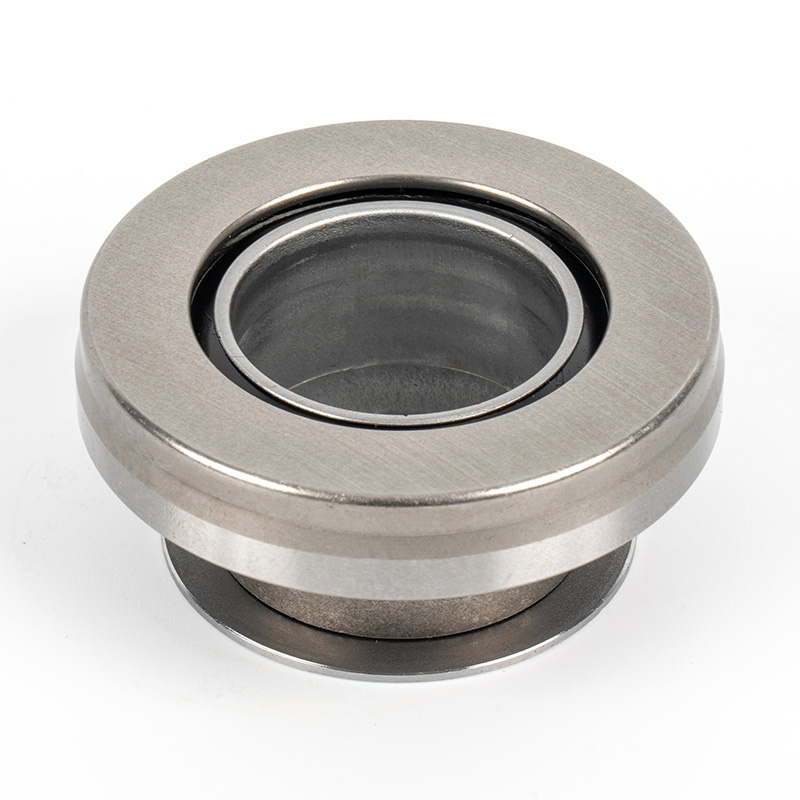
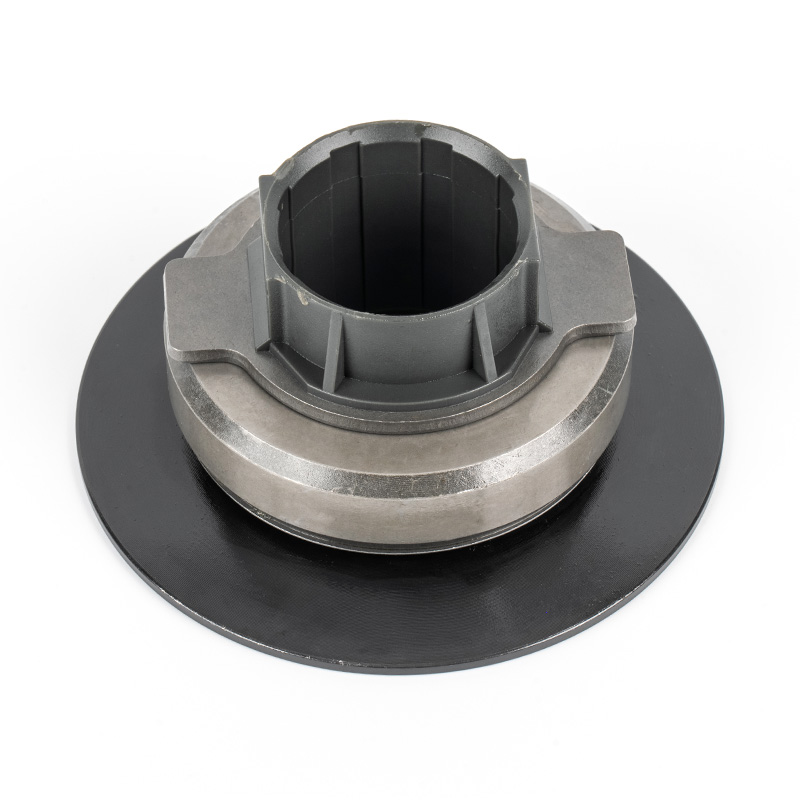
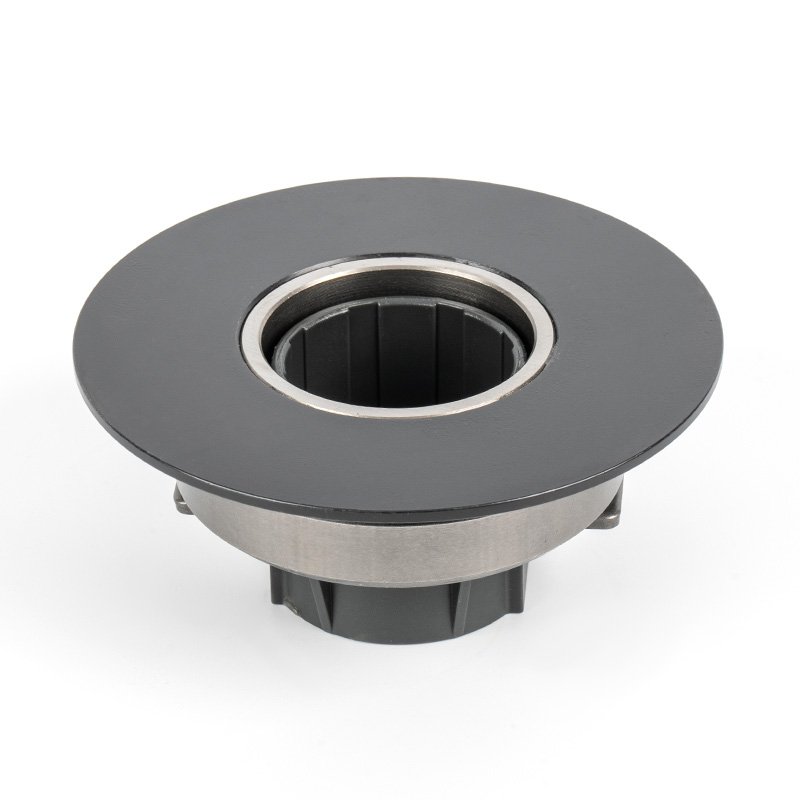
When people discover a problem with their clutch release bearing, their first reaction is often, "Can I still manage to drive it for a while?" While the car might not be completely incapacitated yet, driving with a faulty clutch release bearing is like carrying a ticking time bomb. Here's an analysis of driving with ...
READ MORE-
-
Although clutch release bearings are designed to be durable, they are also quite delicate, and many everyday habits can unknowingly shorten their lifespan. Here are some of the main reasons for their damage: 1. The Habit of Keeping Your Foot on the Clutch Pedal This is the most common cause of bearing damage. Many dr...
READ MORE -
The cost of replacing a clutch release bearing (also commonly called a release bearing or thrust bearing) mainly consists of two parts, but the most painful part is often not the cost of the part itself, but the expensive labor costs. Here's a breakdown of the repair costs: 1. Cost of the part itself Bearing unit pri...
READ MORE
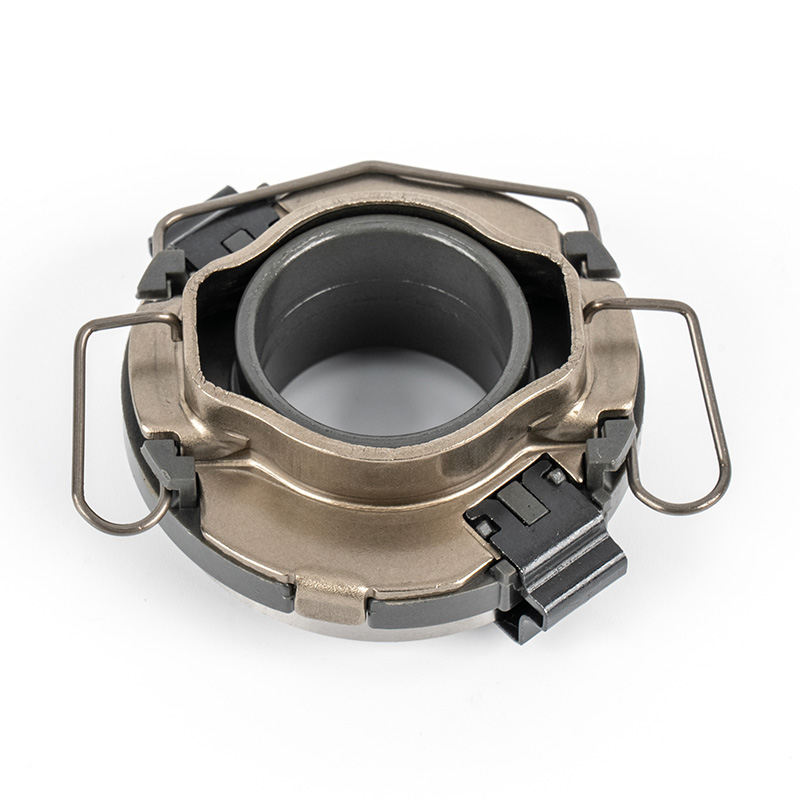
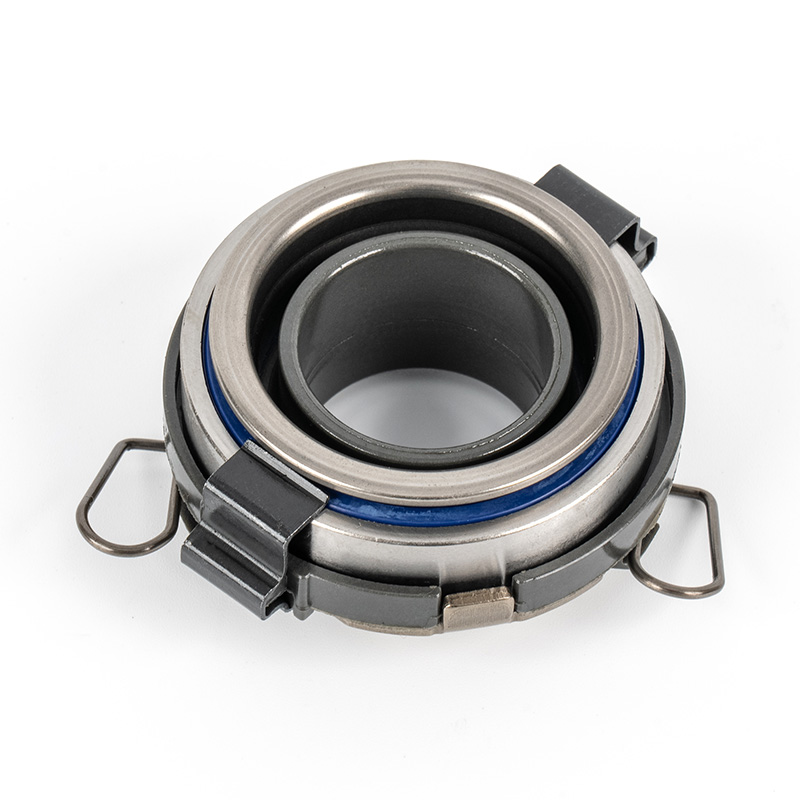
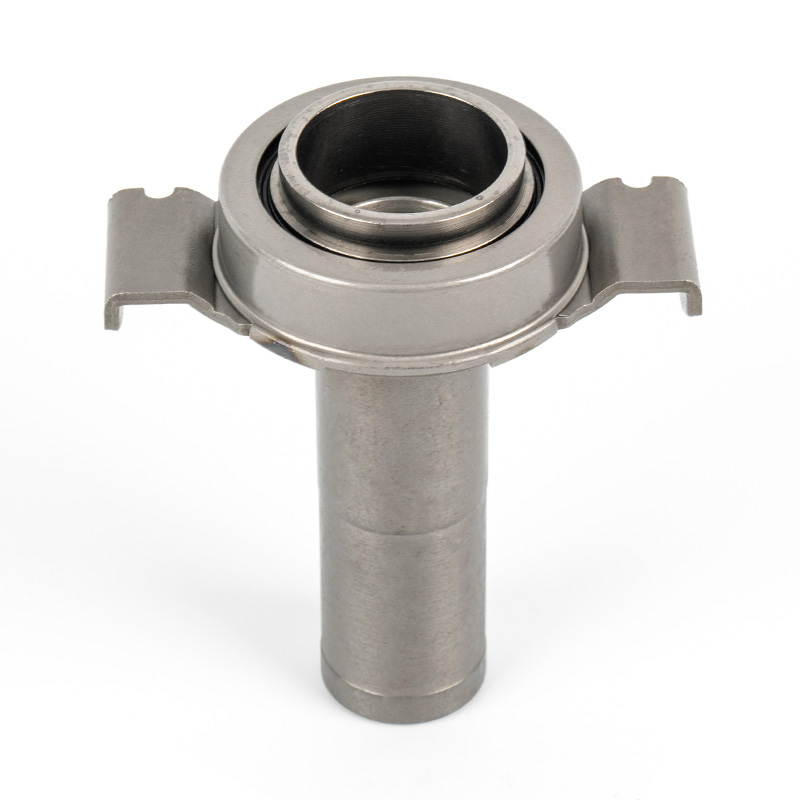
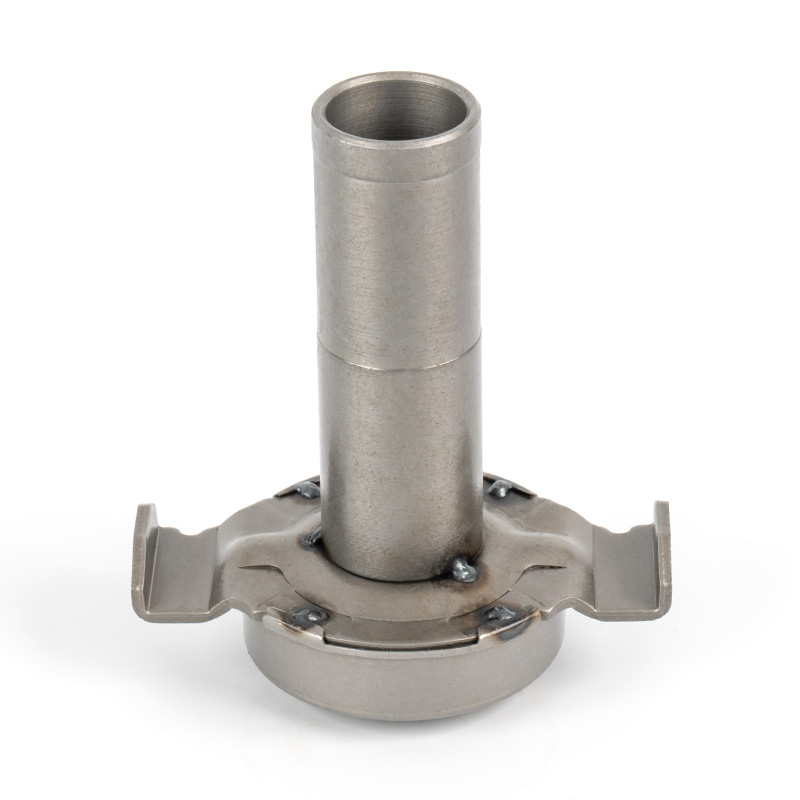
The clutch system is a critical component in manual transmission vehicles, enabling smooth gear shifts and power transfer from the engine to the drivetrain. Within this system, the clutch release bearing plays a pivotal role in ensuring efficient disengagement of the clutch.
What is a Clutch Release Bearing?
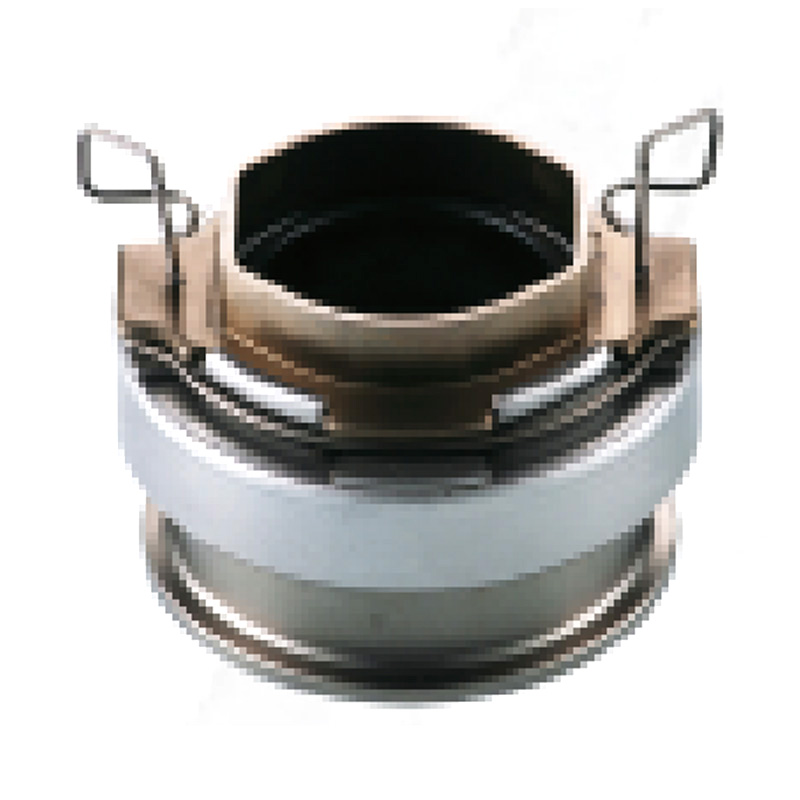
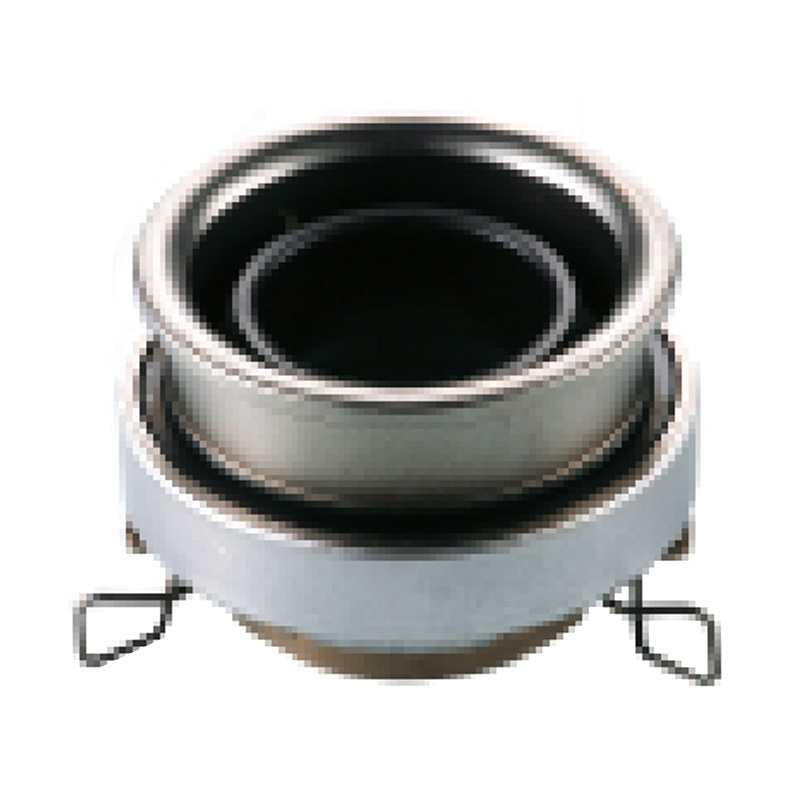
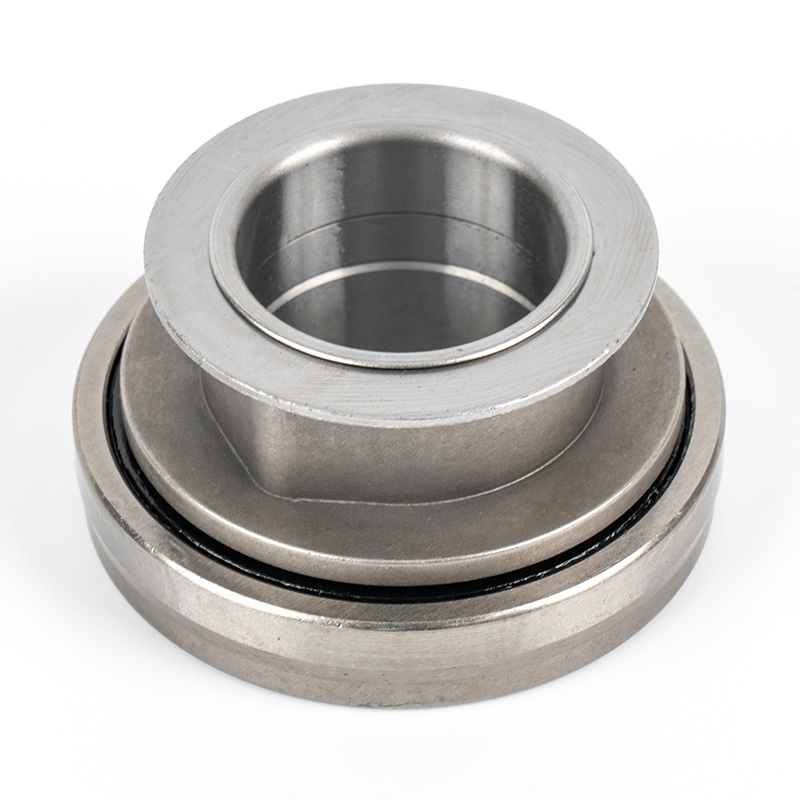
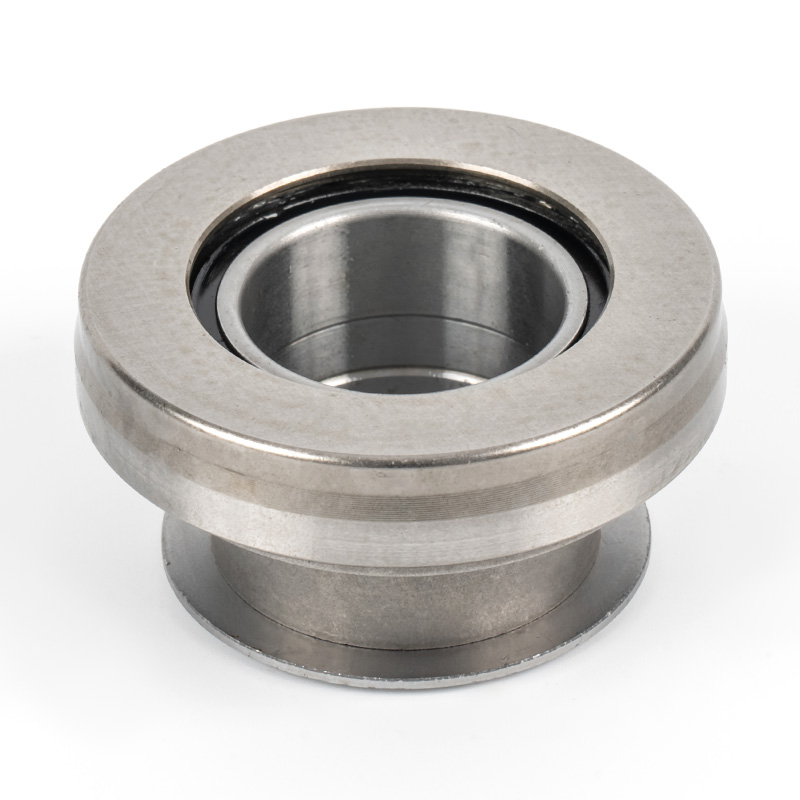
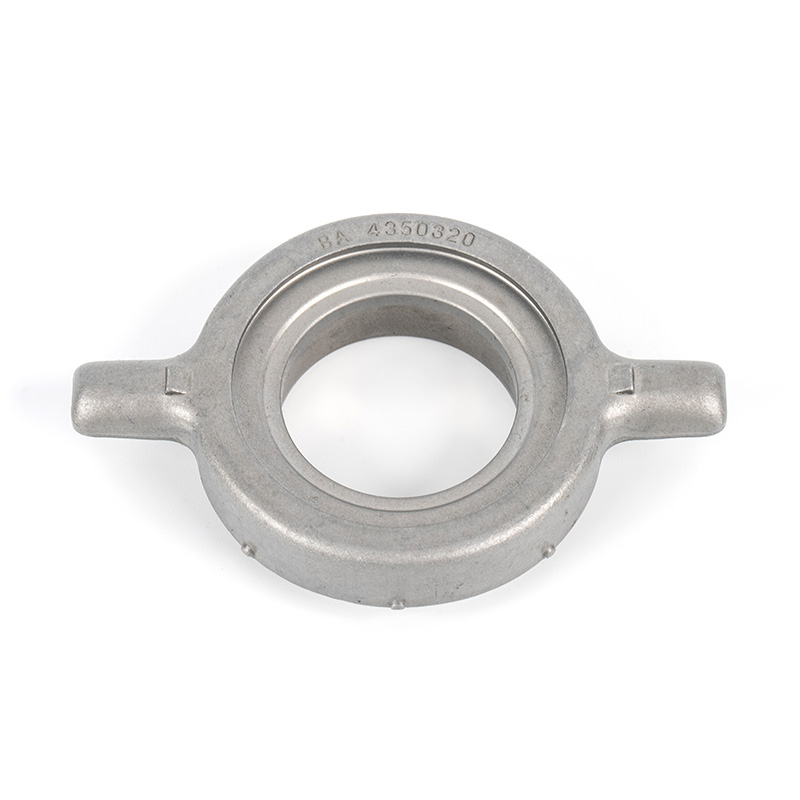
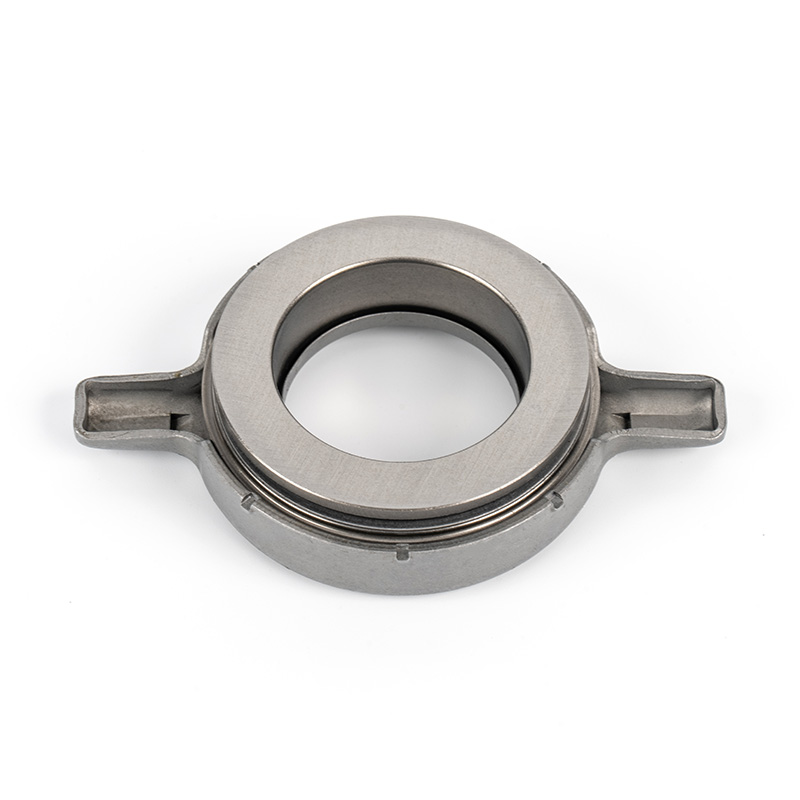
A clutch release bearing, also known as a throwout bearing, is a component in the clutch assembly that facilitates the disengagement of the clutch disc from the flywheel. When the clutch pedal is depressed, the bearing moves forward to apply pressure against the fingers of the clutch diaphragm spring or the release levers. This action separates the clutch disc from the flywheel, interrupting power flow and allowing gear changes. The bearing typically consists of a high-strength steel or composite housing with precision ball or roller bearings to reduce friction and wear during operation.
Types of Clutch Release Bearings
Clutch release bearings are categorized based on their design and actuation mechanisms. The main types include:
Mechanical Release Bearings: These are operated via a cable or linkage system. They are simple in design and commonly found in older or budget-oriented vehicles. Mechanical bearings rely on direct physical force from the clutch pedal.
Hydraulic Release Bearings: Also referred to as concentric slave cylinders, these use hydraulic fluid pressure to actuate the bearing. They are integrated into the clutch release mechanism and offer smoother operation, reducing pedal effort. Hydraulic systems are prevalent in modern vehicles.
Self-Adjusting Bearings: These incorporate mechanisms to automatically compensate for clutch wear, maintaining consistent pedal feel over time. They are often used in high-performance or heavy-duty applications.
Non-Self-Adjusting Bearings: These require manual adjustment to account for clutch disc wear and are typically found in specific industrial or vintage automotive contexts.
How Clutch Release Bearings Work
The operation of a clutch release bearing involves a sequence of mechanical or hydraulic actions:
When the clutch pedal is pressed, force is transmitted through a cable, linkage, or hydraulic system.
The release bearing moves axially toward the clutch pressure plate.
The bearing contacts the diaphragm spring or release levers, causing the pressure plate to retract.
This disengages the clutch disc from the flywheel, halting power transmission.
Upon releasing the pedal, the bearing retracts, allowing the clutch to re-engage.
The bearing must withstand high rotational speeds, axial loads, and thermal stress, necessitating robust materials like hardened steel or ceramic composites.
Applications of Clutch Release Bearings
Clutch release bearings are primarily used in manual transmission systems across various sectors:
Automotive Industry: Installed in passenger cars, trucks, and commercial vehicles to enable gear shifting and clutch control.
Industrial Machinery: Employed in equipment such as tractors, construction vehicles, and manufacturing machines where manual clutches are utilized.
Motorcycles and Heavy-Duty Vehicles: Adapted for specific transmission designs, including wet clutches in motorcycles or dual-clutch systems in performance applications.
The bearing's design may vary based on load capacity, environmental conditions, and durability requirements.
Comparison of Clutch Release Bearing Types
A factual comparison of common bearing types highlights differences in performance and suitability:
Mechanical vs. Hydraulic Bearings:
Mechanical bearings are less complex and easier to repair but may exhibit higher pedal effort and wear over time.
Hydraulic bearings provide reduced pedal effort and smoother engagement due to fluid damping, but they involve more components and potential fluid leakage issues.
Self-Adjusting vs. Non-Self-Adjusting Bearings:
Self-adjusting bearings maintain optimal clutch performance without manual intervention, ideal for applications with frequent use.
Non-self-adjusting bearings are simpler in construction but require periodic adjustments to prevent clutch slippage or premature wear.
Material choices, such as steel versus polymer composites, also influence durability and heat resistance. For instance, steel bearings handle higher loads, while composites may reduce weight and noise.
Common Issues and Maintenance
Clutch release bearings are subject to wear and failure due to their operational demands. Common problems include:
Noise: Grinding or chirping sounds during clutch pedal operation often indicate bearing wear or lubrication failure.
Overheating: Excessive friction can cause thermal degradation, leading to bearing seizure.
Contamination: Dirt or debris ingress accelerates wear, particularly in non-sealed designs.
Maintenance practices involve regular inspection of the clutch system, ensuring proper lubrication, and replacing the bearing at signs of deterioration. In hydraulic systems, checking fluid levels and seal integrity is essential.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the symptoms of a failing clutch release bearing?
Common signs include unusual noises (e.g., grinding or squealing) when the clutch pedal is pressed, difficulty in shifting gears, or a vibrating pedal. These symptoms result from bearing wear or misalignment.
How long does a clutch release bearing typically last?
Lifespan varies based on usage, driving conditions, and design. In average automotive applications, bearings may last between 50,000 to 100,000 miles. Aggressive driving or improper clutch operation can shorten this range.
Can a clutch release bearing be replaced separately?
Yes, but it is often recommended to replace the bearing during clutch system overhauls to ensure compatibility and prevent future issues. Replacement requires disassembling the transmission, which should be performed by qualified technicians.
What factors affect clutch release bearing performance?
Key factors include alignment with the clutch assembly, lubrication quality, operating temperature, and load conditions. Proper installation and adherence to manufacturer specifications are critical.
Are there environmental considerations for clutch release bearings?
Bearings must comply with regulations on materials and disposal. For example, some designs use environmentally friendly lubricants or recyclable materials to minimize ecological impact.
As a specialist in this field, Xinchang Heyang Auto Parts Co., Ltd. manufactures high-performance Clutch Release Bearings designed to meet these rigorous demands. Our products, which include over 300 types of non-standard bearings, are engineered for automobiles from Japan, Korea, Germany, the USA, and others. Supported by advanced production equipment and a robust management system, we maintain an annual output of 1.2 million pieces, with each bearing backed by a quality assurance of 50,000 kilometers or more.
 +86-13867573512
+86-13867573512