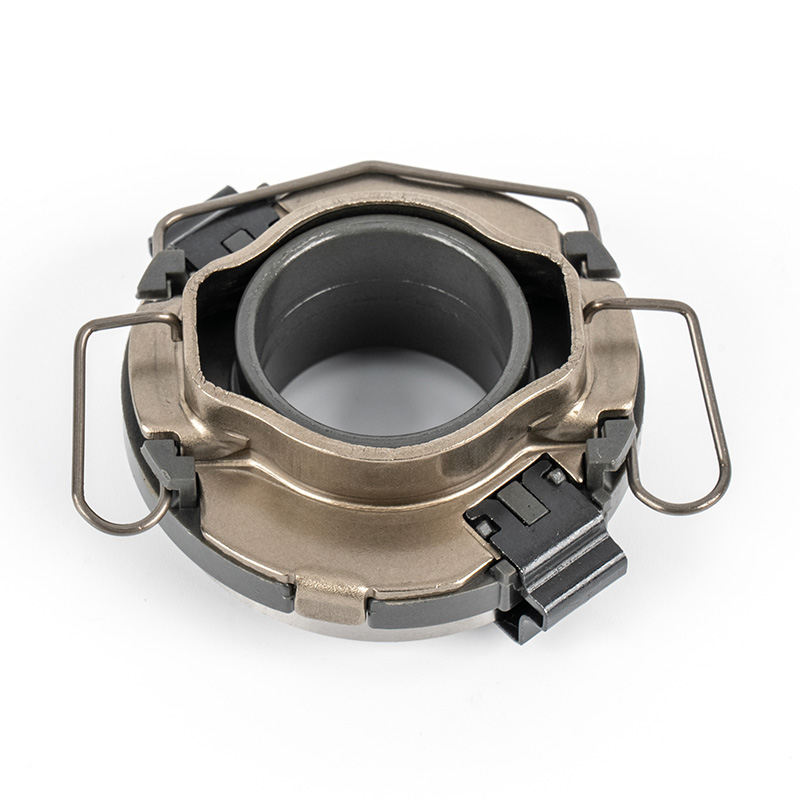
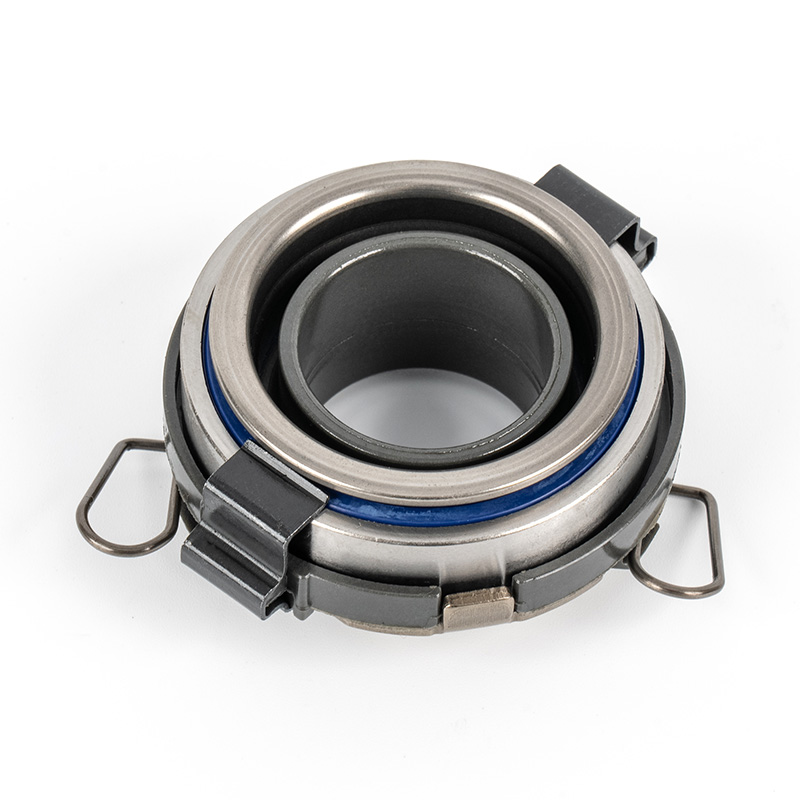
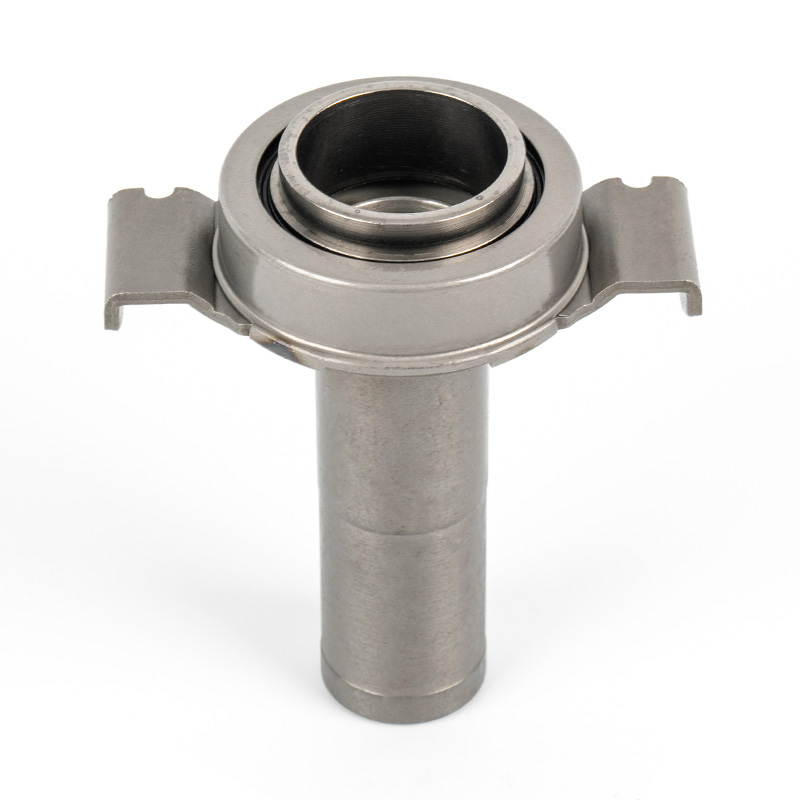
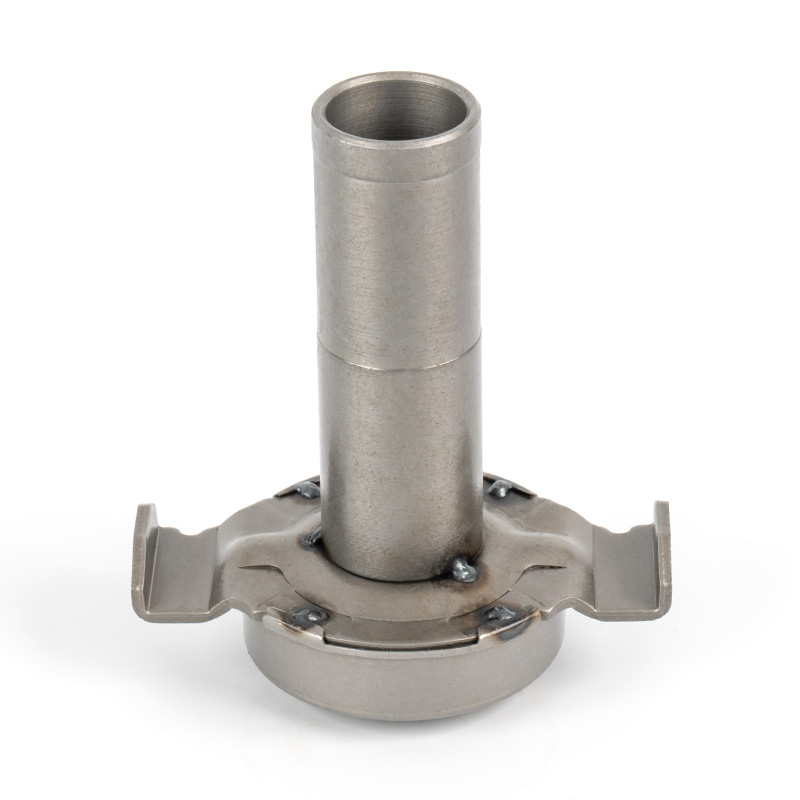
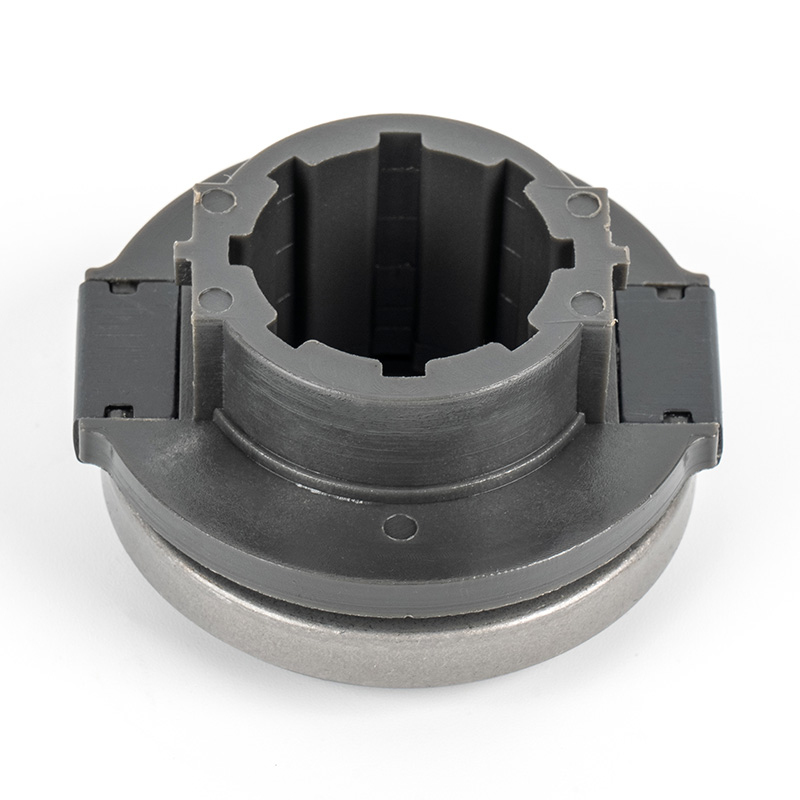
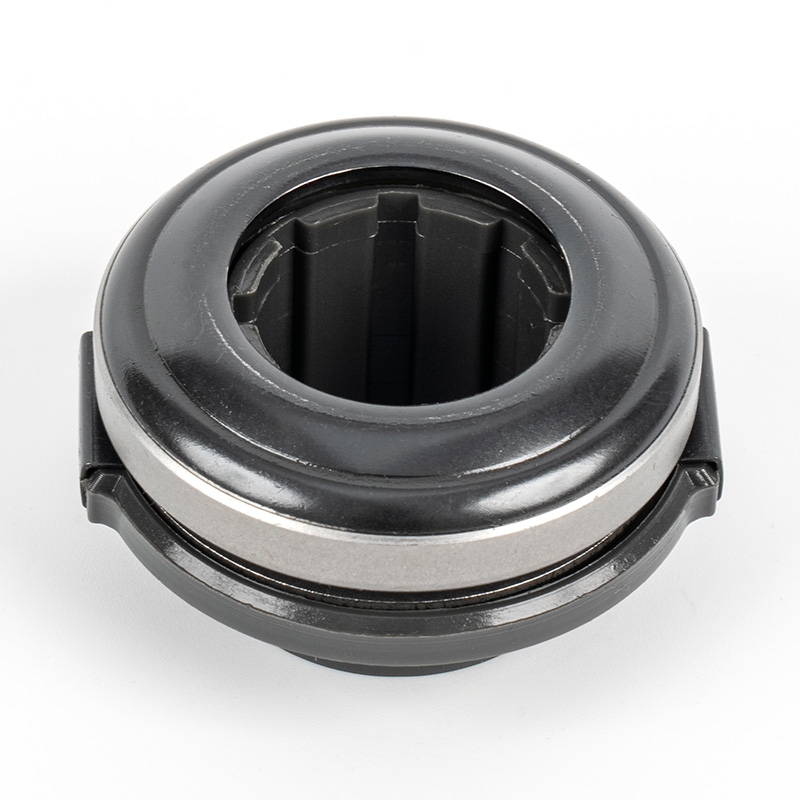
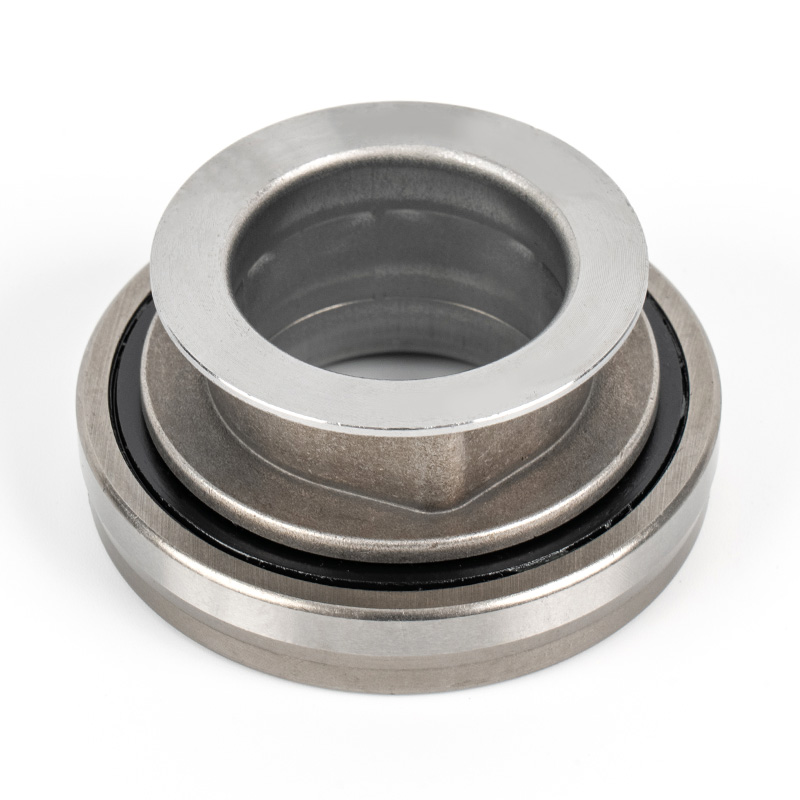
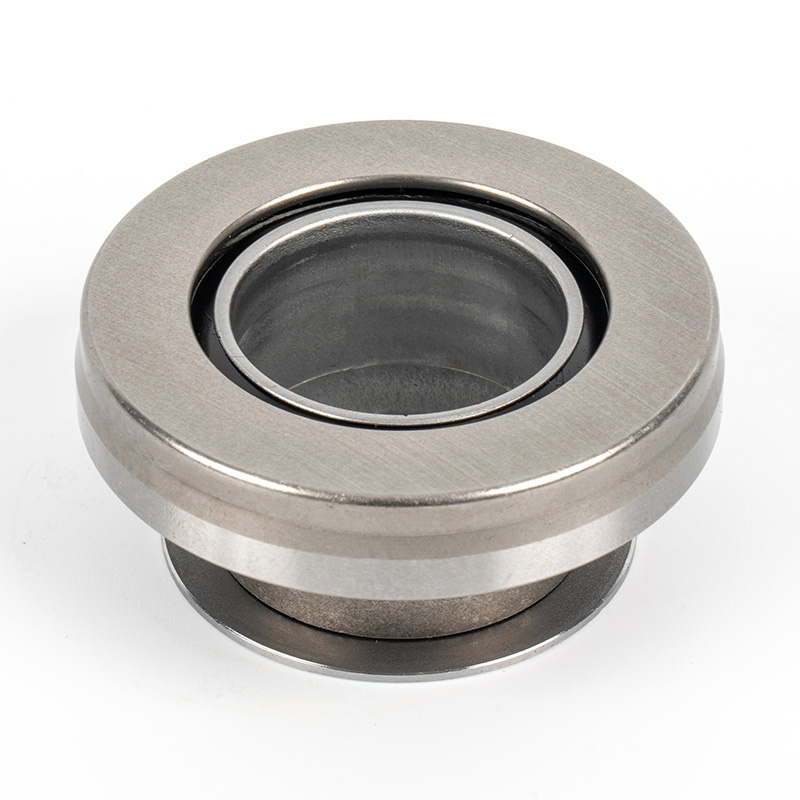
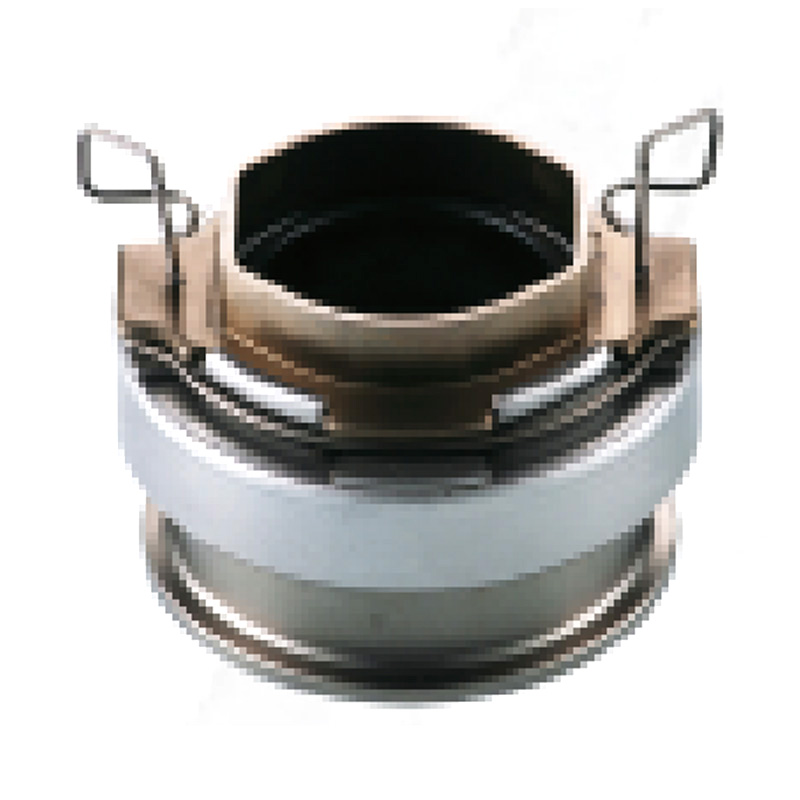
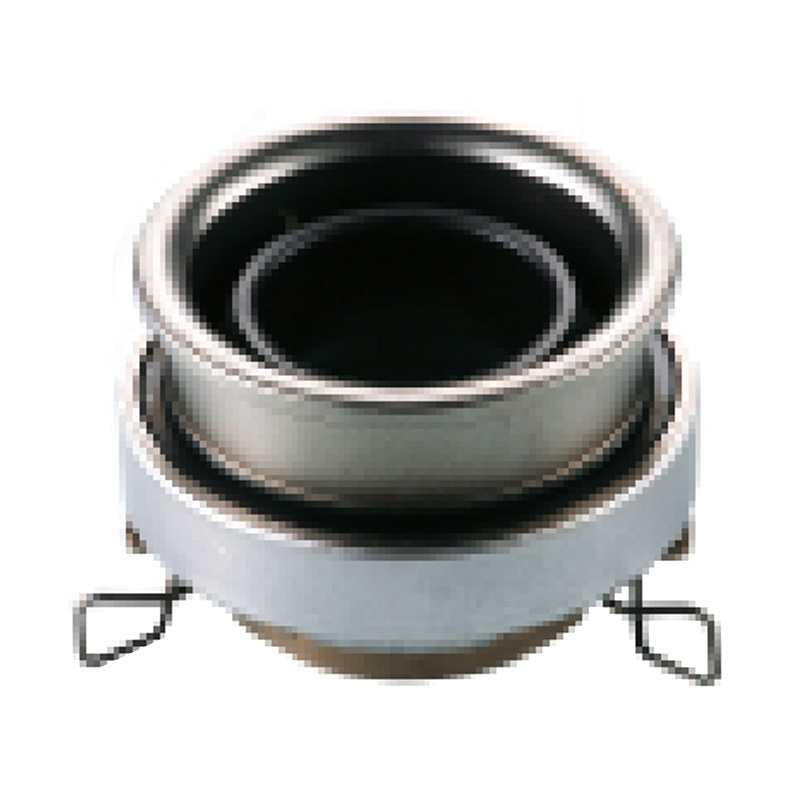
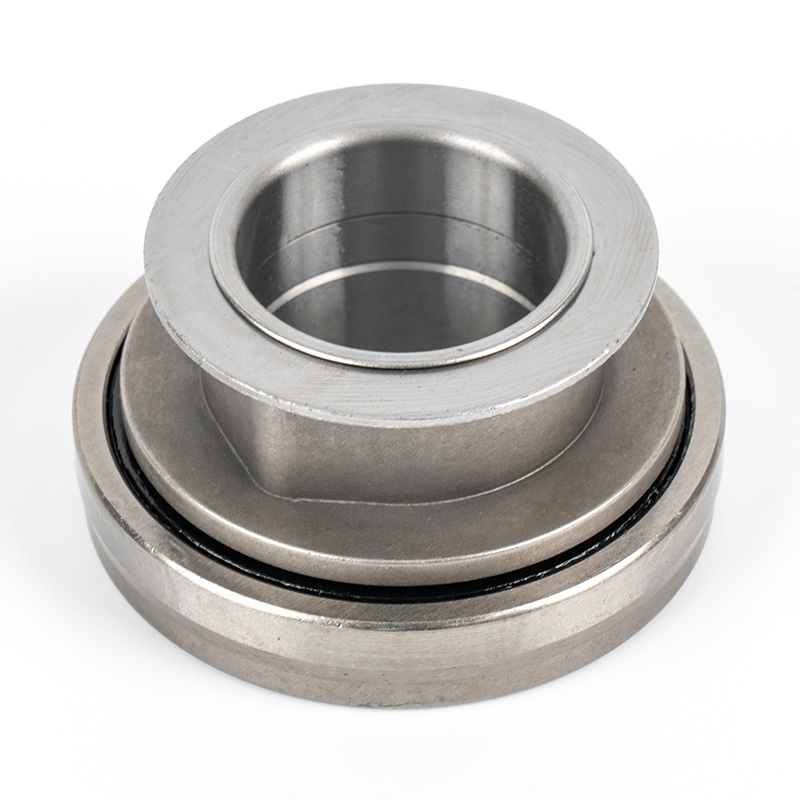
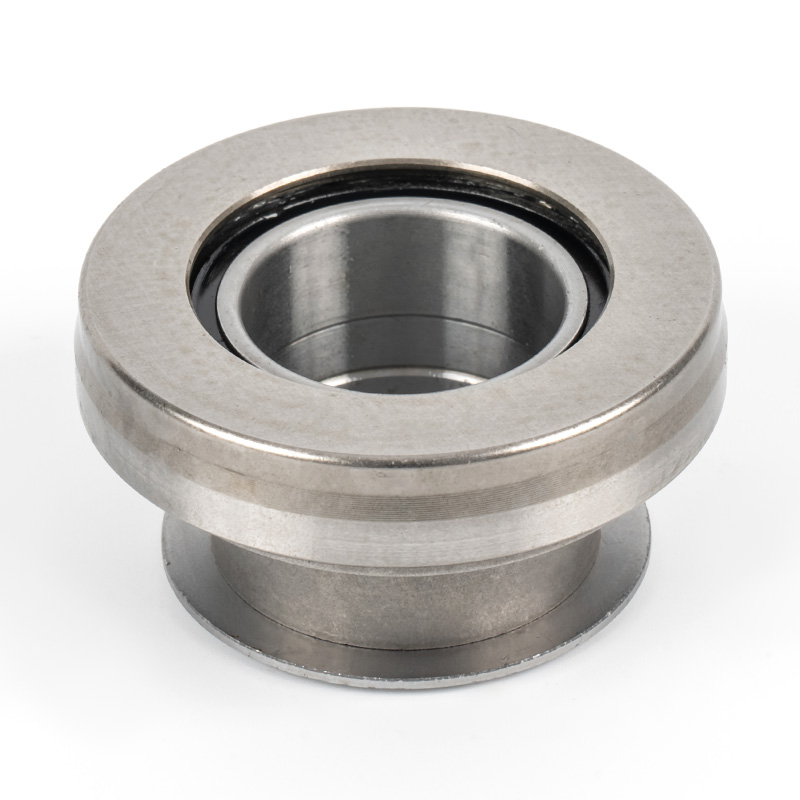
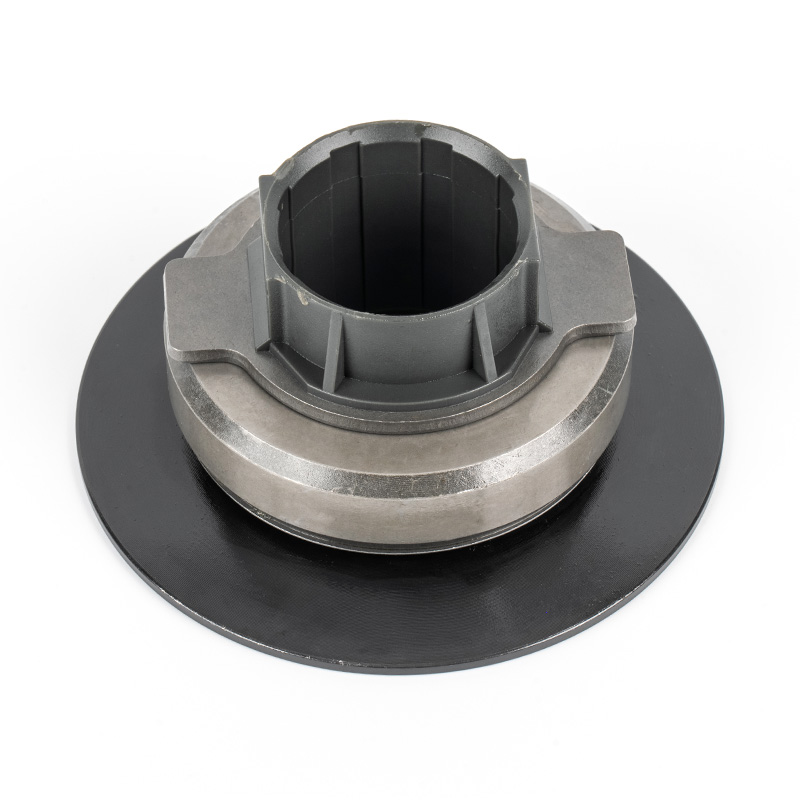
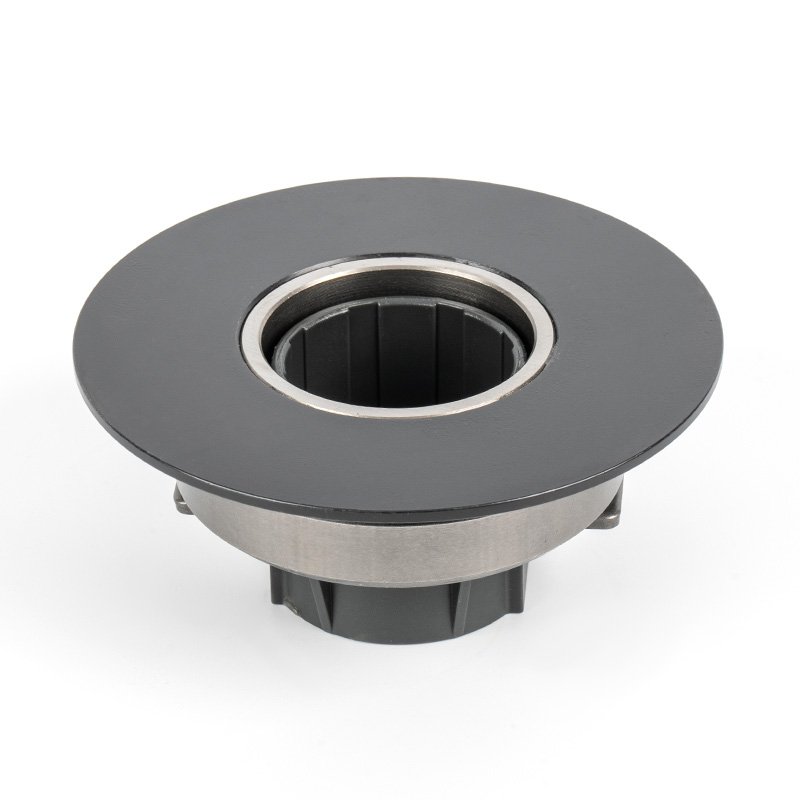
When people discover a problem with their clutch release bearing, their first reaction is often, "Can I still manage to drive it for a while?" While the car might not be completely incapacitated yet, driving with a faulty clutch release bearing is like carrying a ticking time bomb. Here's an analysis of driving with ...
READ MORE-
-
Although clutch release bearings are designed to be durable, they are also quite delicate, and many everyday habits can unknowingly shorten their lifespan. Here are some of the main reasons for their damage: 1. The Habit of Keeping Your Foot on the Clutch Pedal This is the most common cause of bearing damage. Many dr...
READ MORE -
The cost of replacing a clutch release bearing (also commonly called a release bearing or thrust bearing) mainly consists of two parts, but the most painful part is often not the cost of the part itself, but the expensive labor costs. Here's a breakdown of the repair costs: 1. Cost of the part itself Bearing unit pri...
READ MORE
Automotive bearings are critical components in vehicles, designed to enable smooth rotational motion, reduce friction, and support mechanical loads. They are integral to the performance, safety, and efficiency of automobiles—from passenger cars to commercial vehicles.
Xinchang Heyang Auto Parts Co., Ltd. specializes in the production of Automotive Clutch Release Bearings and over 300 types of non-standard bearings, mainly applicable to vehicles from Japan, Korea, Germany, the USA, and other regions. With advanced production equipment and a comprehensive management system, the company achieves an annual production capacity of 1.2 million pieces, backed by a product quality assurance of up to 50,000 kilometers or more.
Concept of Automotive Bearings
A bearing is a machine element that constrains relative motion to only the desired direction while reducing friction between moving parts. In automotive contexts, bearings manage radial and axial loads in rotating assemblies, such as wheels, engines, and transmissions. They operate on principles of rolling contact (e.g., ball or roller bearings) or sliding contact (e.g., plain bearings), with lubrication often used to minimize wear and heat generation. Key functions include load support, precision alignment, and vibration damping, contributing to vehicle stability and longevity.
Types of Automotive Bearings
Automotive bearings are categorized based on design, load capacity, and application requirements. Common types include:
Ball Bearings: Utilize spherical balls to handle moderate radial and axial loads. Examples include deep-groove ball bearings for wheels and electric motors.
Roller Bearings: Employ cylindrical, tapered, or spherical rollers for higher load capacities. Tapered roller bearings are often used in wheel hubs and differentials.
Needle Bearings: Feature thin, long rollers for compact spaces, such as in transmissions and universal joints.
Plain Bearings: Also known as bushings, these use sliding surfaces and are found in engine components like connecting rods.
Hub Bearing Units: Integrated assemblies that combine bearings, seals, and mounting features for modern wheel applications, improving ease of installation and performance.
Each type is engineered for specific conditions, such as speed, temperature, and environmental exposure, with materials ranging from steel to advanced polymers and ceramics.
Applications in the Automotive Industry
Bearings are ubiquitous in vehicles, with key applications including:
Wheel Assemblies: Hub bearings support vehicle weight and enable smooth wheel rotation, directly impacting handling and safety.
Engine Systems: Crankshaft and camshaft bearings reduce friction in internal combustion engines, enhancing efficiency and durability.
Transmissions and Gearboxes: Bearings facilitate gear shifting and power transmission, with needle bearings common in manual transmissions.
Steering and Suspension: Bearings in steering columns and shock absorbers ensure precise control and comfort.
Electric Vehicles (EVs): Specialized bearings are used in electric motors and battery cooling systems, addressing challenges like high speeds and electromagnetic interference.
These applications require bearings to meet stringent standards for noise, vibration, and harshness (NVH), as well as longevity under varying operational conditions.
Comparison of Bearing Types
The selection of bearings depends on factors such as load type, speed, and space constraints. A comparative analysis includes:
Load Capacity: Roller bearings generally support higher radial loads than ball bearings, while tapered roller bearings excel in combined radial and axial loads. Plain bearings are suitable for high-load, low-speed scenarios.
Speed Limitations: Ball bearings typically allow higher rotational speeds due to lower friction, whereas roller bearings may be preferred for heavy-duty, low-speed applications.
Durability and Maintenance: Sealed or pre-lubricated bearings (e.g., hub units) require less maintenance, but plain bearings may need periodic lubrication.
Cost and Complexity: Standard ball bearings are often cost-effective for general use, while customized hub units can reduce assembly time but may involve higher initial costs.
This comparison is based on engineering principles, and actual performance varies with design, material quality, and operating conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the typical lifespan of an automotive bearing?
Lifespan depends on factors like load, speed, lubrication, and environmental conditions. In wheel applications, bearings may last over 150,000 kilometers under normal driving conditions, but premature failure can occur due to contamination or improper installation.
What are common signs of bearing failure?
Indicators include unusual noises (e.g., grinding or humming), vibration, uneven tire wear, and steering instability. Early detection through regular maintenance can prevent further damage.
How are bearings maintained in vehicles?
Maintenance involves inspection for wear, ensuring proper lubrication, and replacing sealed units when necessary. For hub bearings, follow manufacturer guidelines, as many are designed as non-serviceable assemblies.
Can bearings be used in electric vehicles?
Yes, bearings in EVs often require adaptations for higher speeds, reduced lubrication, and compatibility with electric motor environments, such as insulating materials to prevent electrical erosion.
What standards govern automotive bearing production?
Bearings are manufactured according to international standards (e.g., ISO, DIN) and industry-specific regulations to ensure quality, safety, and interoperability.
 +86-13867573512
+86-13867573512